What are brake pads?
 2025.08.14
2025.08.14
 Industry News
Industry News
Brake pads are a critical safety component in a vehicle's braking system. Their function is to convert the vehicle's kinetic energy into heat through friction with the rotating brake disc or drum, thereby slowing or stopping the vehicle. As a core component of the brake system, the performance of the brake pad is directly related to driving safety and the driving experience. Its performance directly affects stopping distance, noise control, and thermal stability.
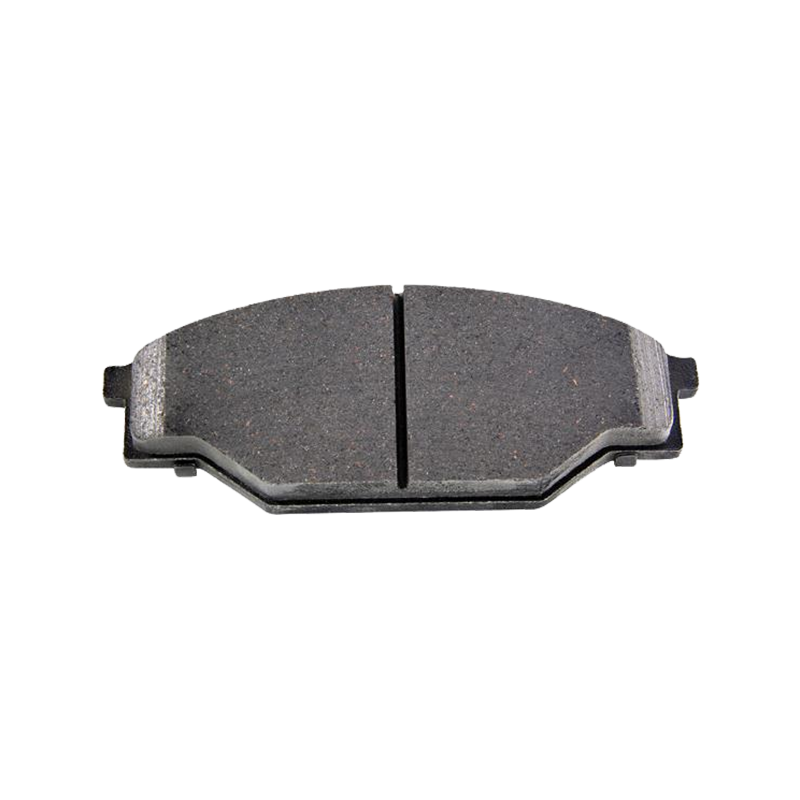
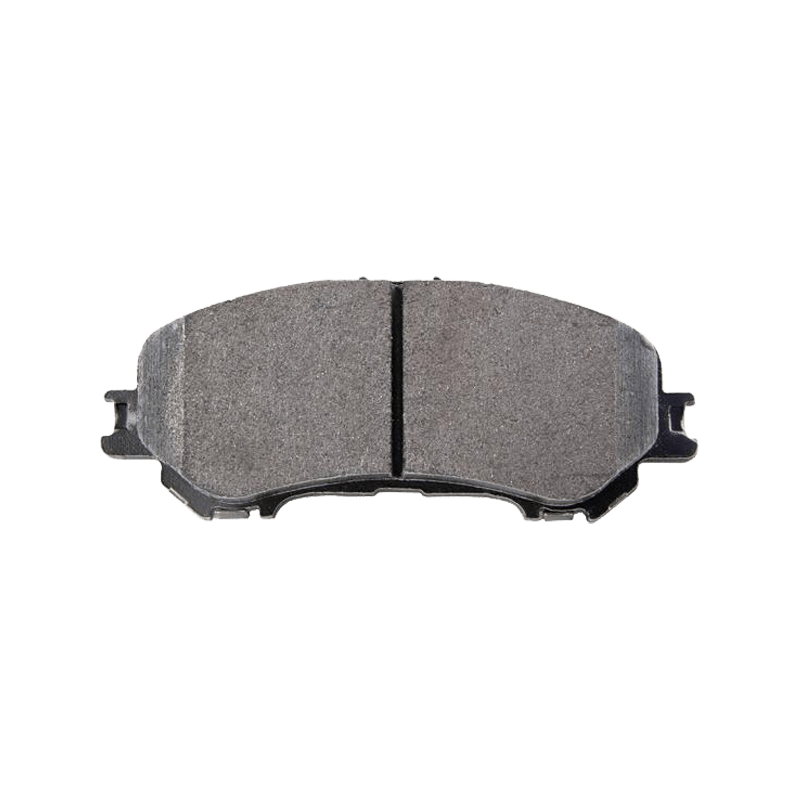
Structurally, brake pads primarily consist of a friction material layer, a metal backing plate, and additional functional layers. The friction material layer, the part that actually engages in braking, is made from a variety of composite materials using a high-temperature and high-pressure process. These include metal fibers, ceramic particles, and organic resins. The metal backing plate provides structural support, ensuring the brake pad retains its shape under high pressure. Functional features such as the muffler and thermal insulation layer reduce vibration and noise and prevent heat transfer to the brake cylinder.
Depending on the material formulation, brake pads are primarily categorized into four types: semi-metallic, low-metallic, ceramic, and organic. Semi-metallic brake pads contain 30%-65% metal, providing strong braking force but prone to noise and dust generation. Low-metal pads reduce metal content, improving braking smoothness. Ceramic brake pads, primarily made of ceramic fiber, offer quietness, low dust production, and high-temperature resistance, but are more expensive. Organic brake pads (NAO) utilize a non-metallic formulation, offering excellent environmental performance but slightly less high-temperature stability.
In actual use, brake pad performance is influenced by multiple factors. The coefficient of friction is the most critical parameter, typically ranging from 0.35 to 0.45 to achieve a balance between braking efficiency and control linearity. Temperature characteristics determine the performance of the brake pad under continuous braking. Ordinary consumer brake pads can withstand temperatures around 300°C, while competition brake pads can maintain stability at 800°C. Wear rate, noise control, and compatibility with the brake disc are also important indicators of brake pad quality.
For vehicle owners, regularly checking brake pad thickness (recommended remaining thickness of at least 3mm), paying attention to abnormal noise and changes in braking distance, and selecting certified brake pads that match the vehicle's original design are key to ensuring reliable braking. Especially after vigorous driving or mountainous driving, the condition of the brake pads should be checked promptly to prevent excessive wear that could affect driving safety. As one of the most frequently replaced safety components on a vehicle, high-quality brake pads not only guarantee safe driving but also provide a vital commitment to vehicle and pedestrian safety.
 Search
Search
 Eng
Eng 
 English
English Español
Español Português
Português