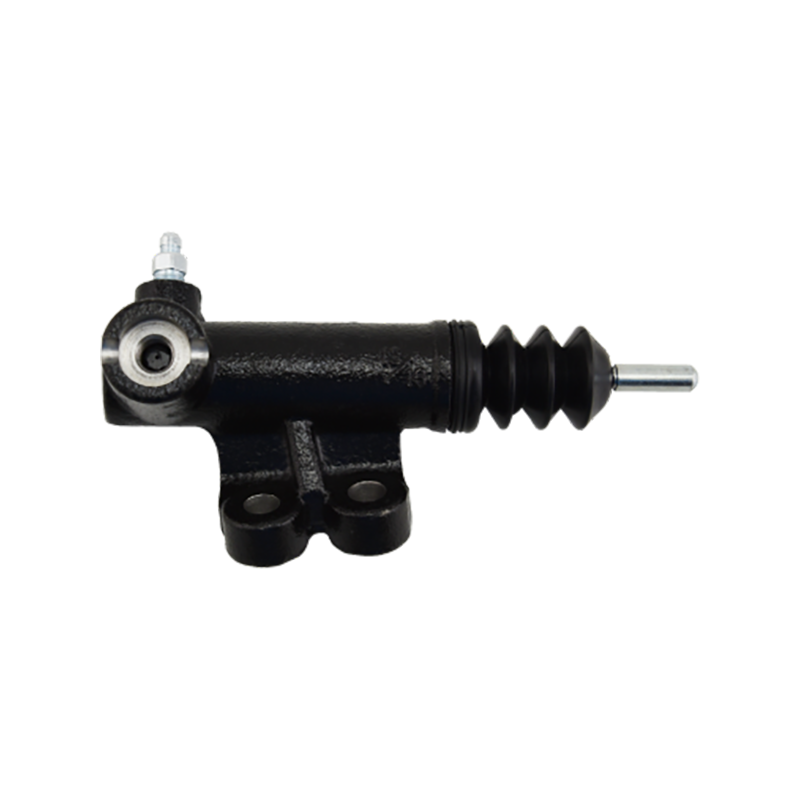
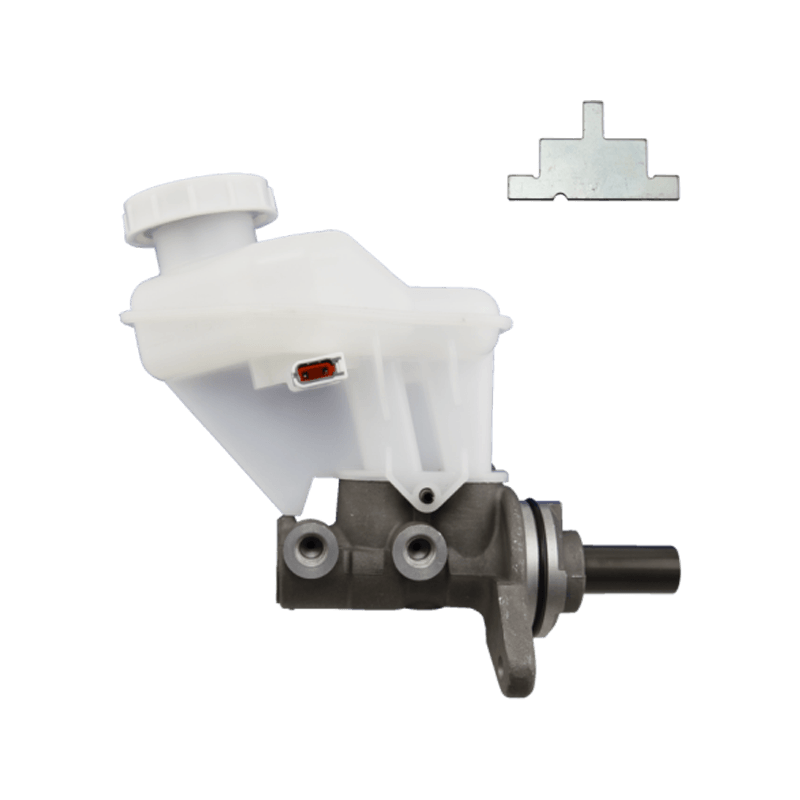
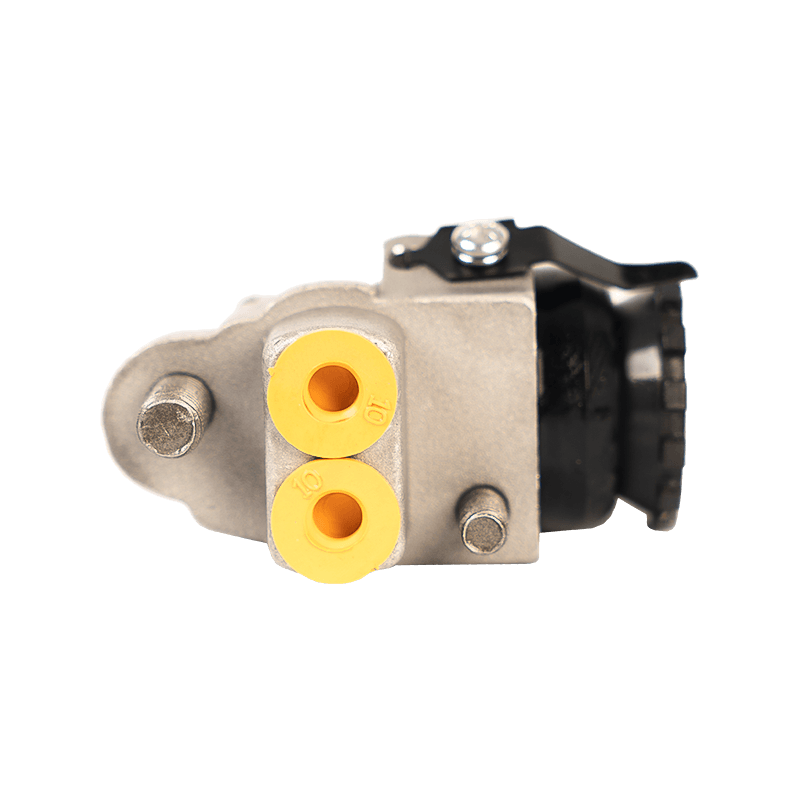
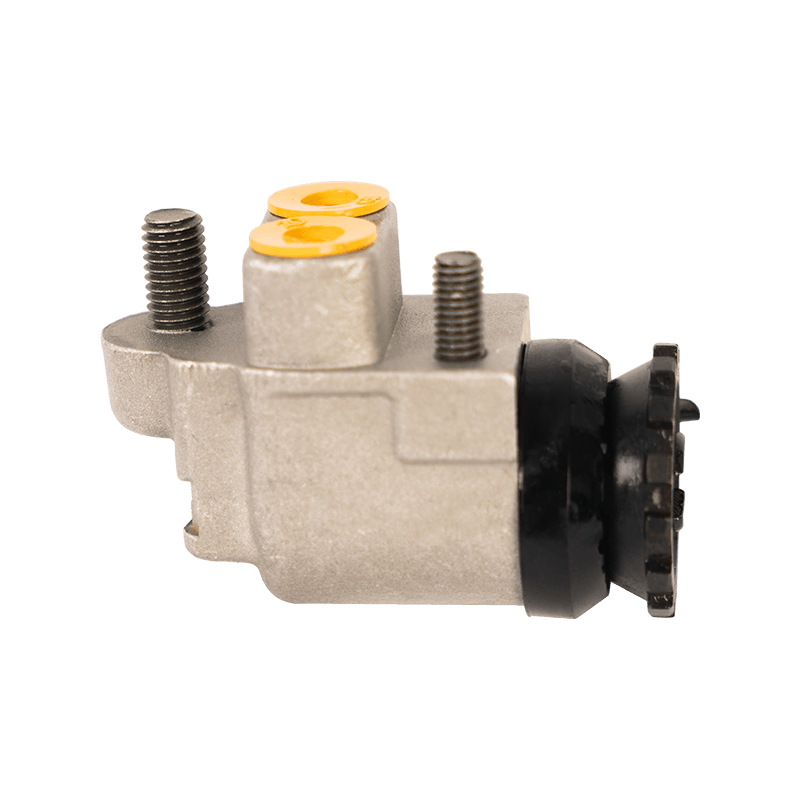
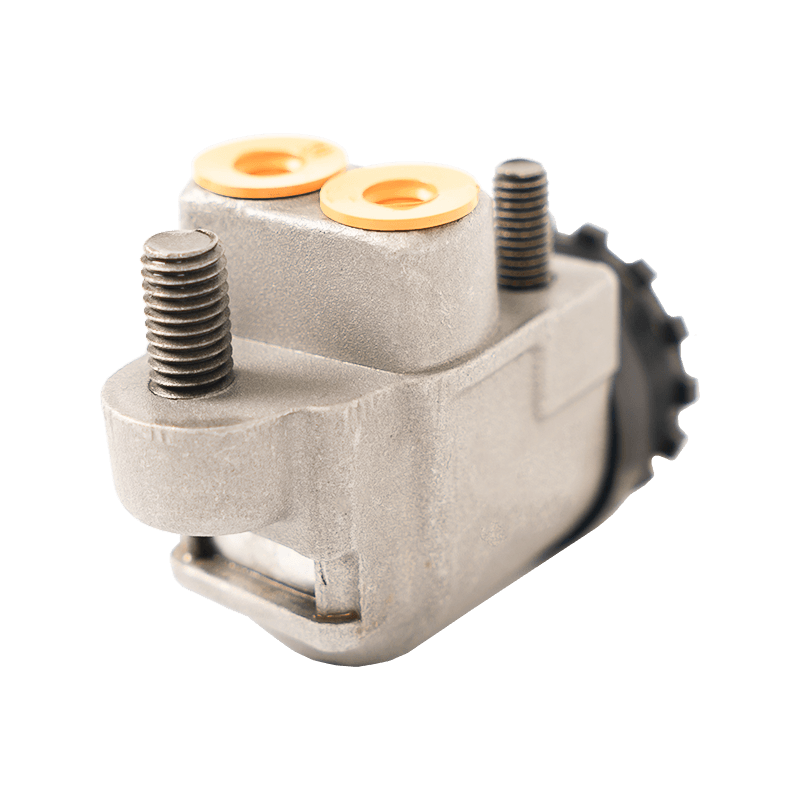
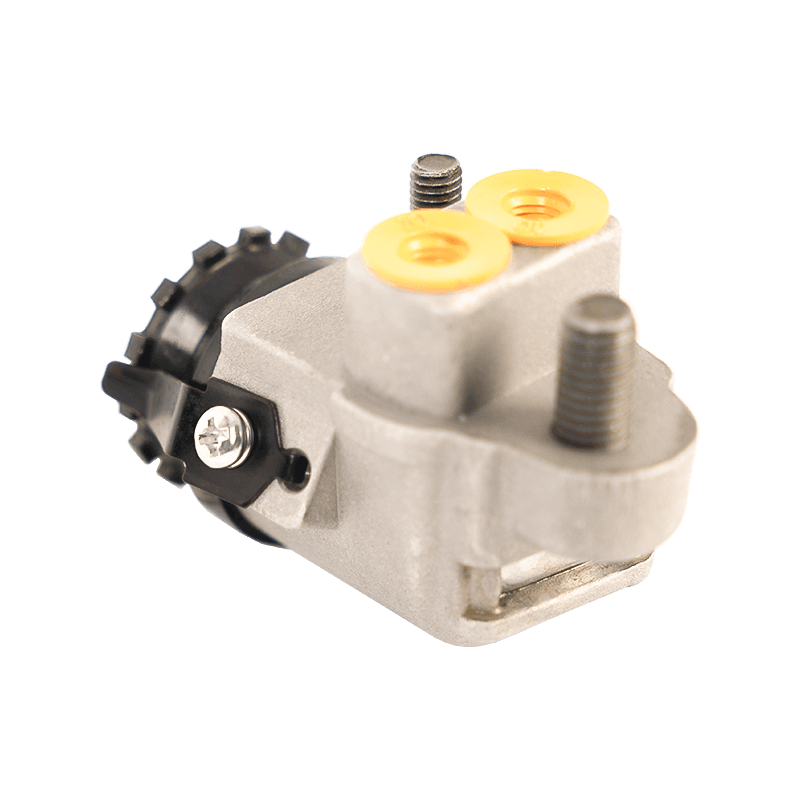
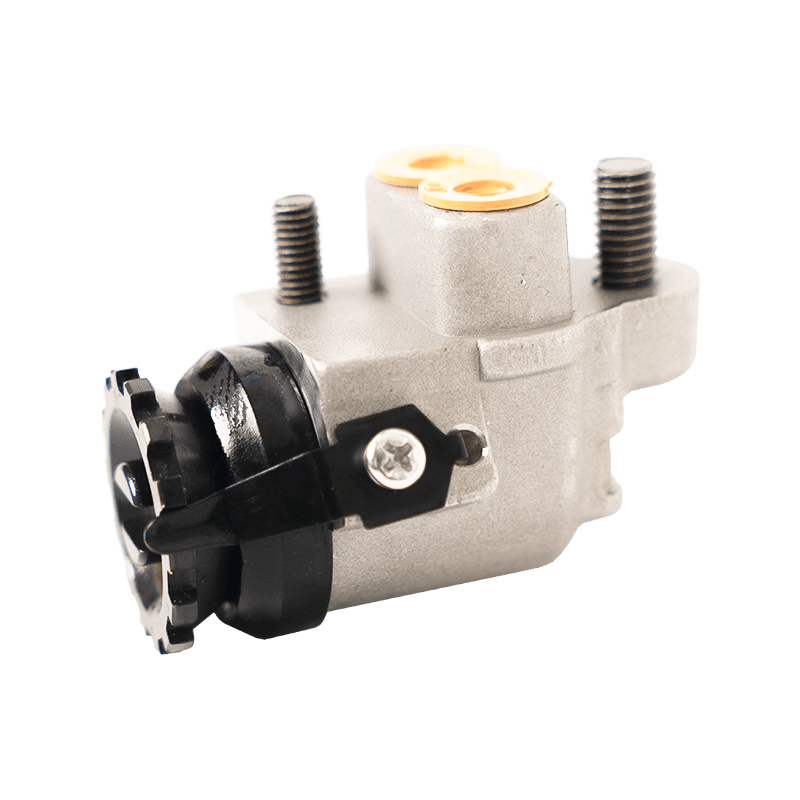
47510-87204 Brake Wheel Cylinder for DAIHATSU
It is usually mounted on the axle, near the wheel that is to be equipped for braking. Air pressure is fed through an inlet port. The air pushes against the diaphragm and the push rod. The push rod is connected by a clevis and pin to a crank arm-type lever called a 'slack adjuster.
|
OE NO |
47510-87204 |
|
MODEL |
DAIHATSU |

Specifications
KEEP IN TOUCH

We have more than 1,000 brake shoes and brake pads for European, American, Russian, Japanese and Korean cars. The associated factories have created a highly experienced manufacturing team that exports thousands of auto part products worldwide. High quality and competitive prices are our targets. Our products have gained the certifications of ISO9001 and TS16949. We have built up a solid reputation with our customers in more than 30 countries.
We are looking forward to having a brighter and more successful business in the near future together with all of our clients all over the world.
-
Why Choose OE Quality Brake Pads? When selecting brake pads, OE QUALITY BRAKE PADS ensure precise fit, optimal braking performance, and long-term dur...
READ MORE -
What is a Hydraulic Brake Master Cylinder? The hydraulic brake master cylinder is a critical component in a vehicle's braking system. It converts the...
READ MORE -
Why OE Quality Brake Pads Are the Best Choice for Your Car OE (Original Equipment) quality brake pads are specifically designed to match the specific...
READ MORE -
The direct answer: Yes. High-quality brake pads can reduce braking distance by 15%–30%, improve heat resistance, and significantly enhance driving saf...
READ MORE
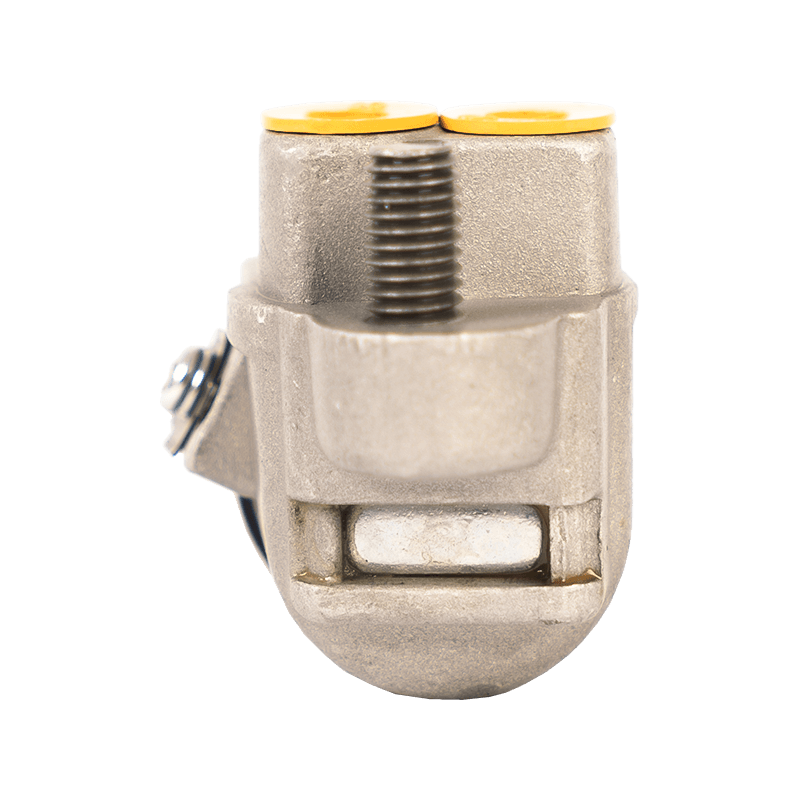
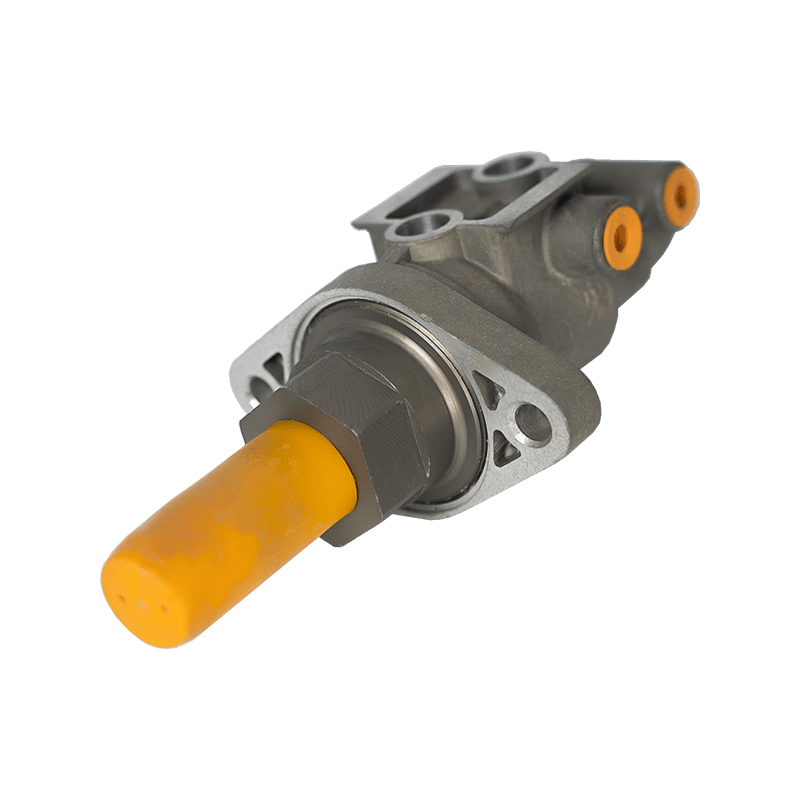
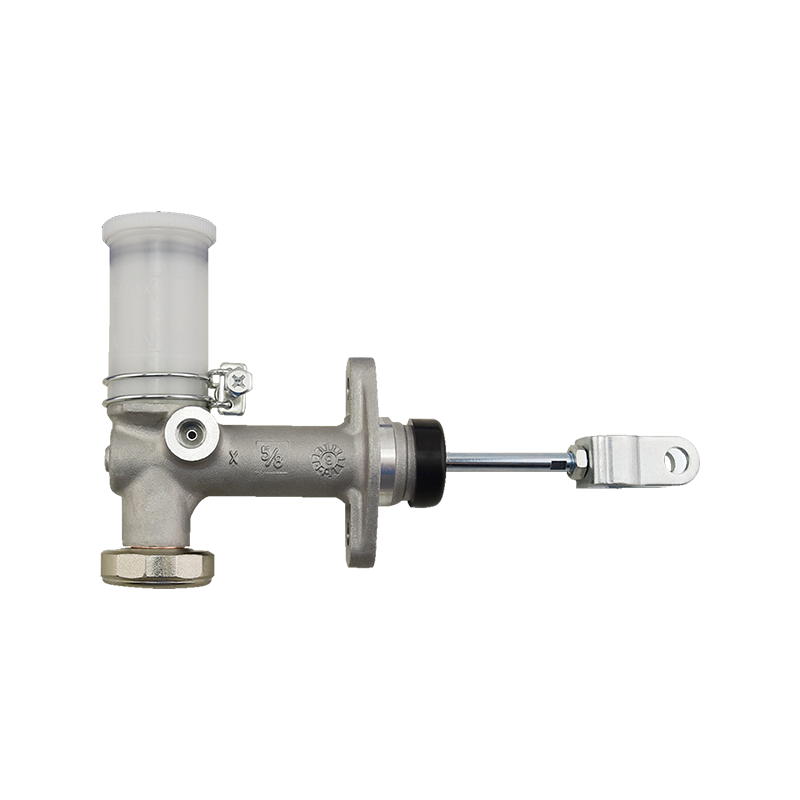
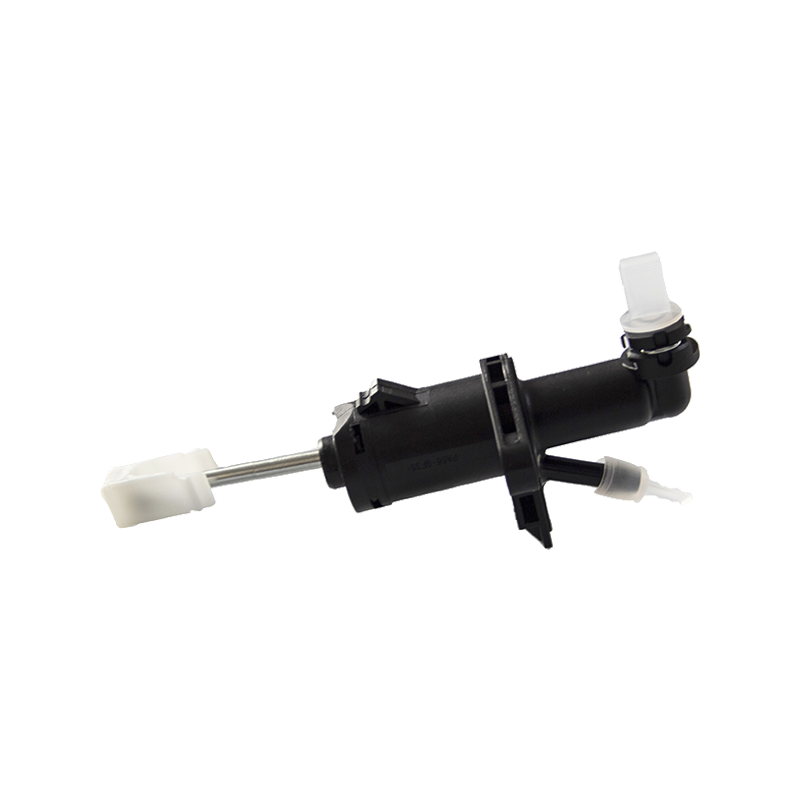
As the core component of the braking system of Daihatsu Automobile, the 47510-87204 brake cylinder plays an indispensable role in the field of chassis braking with its precision engineering design and reliability. The cylinder is specially developed for Daihatsu's micro-commercial vehicle and passenger car platforms, and is suitable for the disc or drum brake system of the front and rear wheels of the vehicle. Its core function is to convert hydraulic energy into mechanical energy, and to achieve smooth deceleration and emergency braking of the vehicle by pushing the brake pads to close contact with the brake disc/drum.
In terms of design and material technology, 47510-87204 adopts a high-strength aluminum alloy casting process, and the internal piston surface is formed with a silicon nitride coating through a chemical vapor deposition process, with a hardness of 1400HV and a high temperature resistance threshold exceeding 550℃, which effectively suppresses the thermal decay phenomenon caused by frequent braking. In actual applications, the slave cylinder also shows good product compatibility and is suitable for many mini commercial vehicles and passenger vehicles such as Daihatsu Hijet and Move.
In terms of maintenance, it is recommended to lubricate and maintain the slave cylinder piston every 30,000 kilometers, check the integrity of the dust cover, and use DOT4 and above standard brake fluid for regular replacement. For high-intensity use scenarios (such as freight vehicles), the inspection cycle needs to be shortened to 15,000 kilometers, focusing on monitoring the smoothness of the piston movement and the sealing of the hydraulic pipeline.
 Search
Search
 Eng
Eng 
 English
English Español
Español Português
Português