Specifications
KEEP IN TOUCH

We have more than 1,000 brake shoes and brake pads for European, American, Russian, Japanese and Korean cars. The associated factories have created a highly experienced manufacturing team that exports thousands of auto part products worldwide. High quality and competitive prices are our targets. Our products have gained the certifications of ISO9001 and TS16949. We have built up a solid reputation with our customers in more than 30 countries.
We are looking forward to having a brighter and more successful business in the near future together with all of our clients all over the world.
-
Why Choose OE Quality Brake Pads? When selecting brake pads, OE QUALITY BRAKE PADS ensure precise fit, optimal braking performance, and long-term dur...
READ MORE -
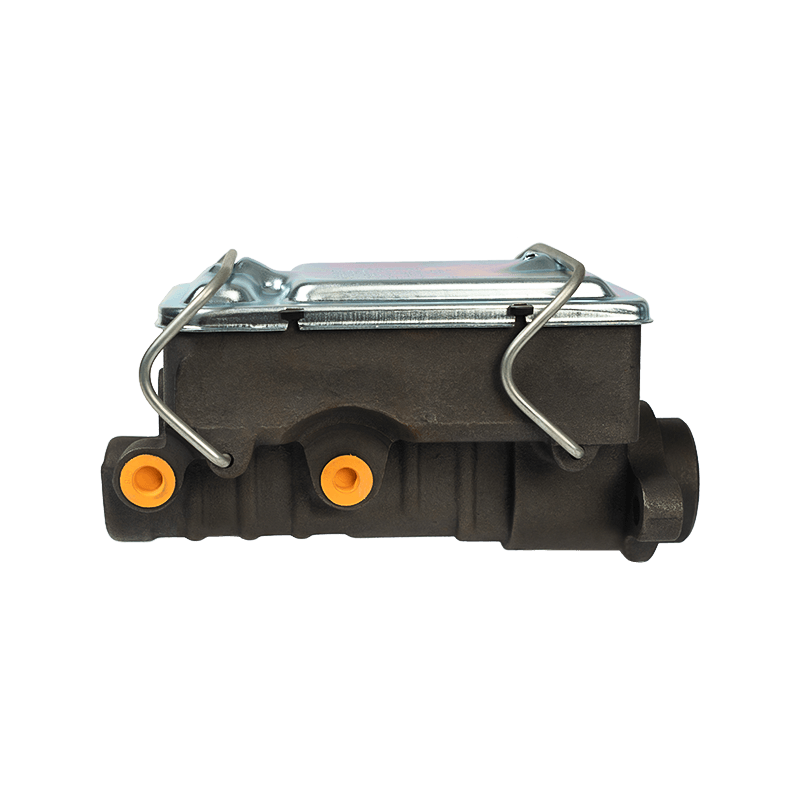
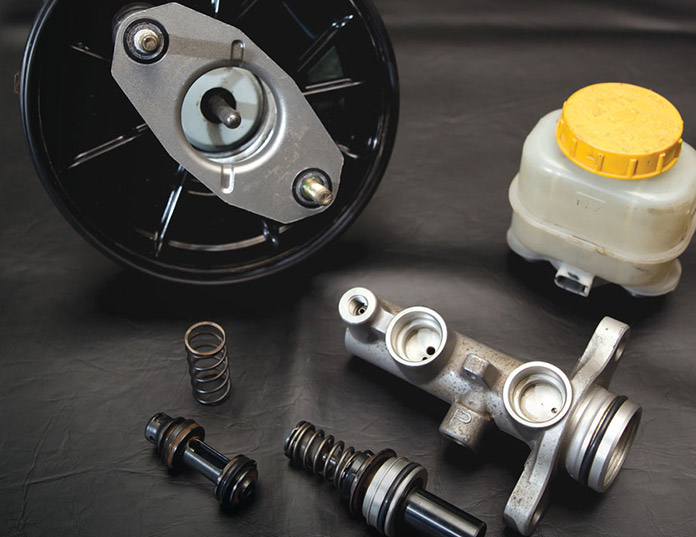
What is a Hydraulic Brake Master Cylinder? The hydraulic brake master cylinder is a critical component in a vehicle's braking system. It converts the...
READ MORE -
Why OE Quality Brake Pads Are the Best Choice for Your Car OE (Original Equipment) quality brake pads are specifically designed to match the specific...
READ MORE -
The direct answer: Yes. High-quality brake pads can reduce braking distance by 15%–30%, improve heat resistance, and significantly enhance driving saf...
READ MORE
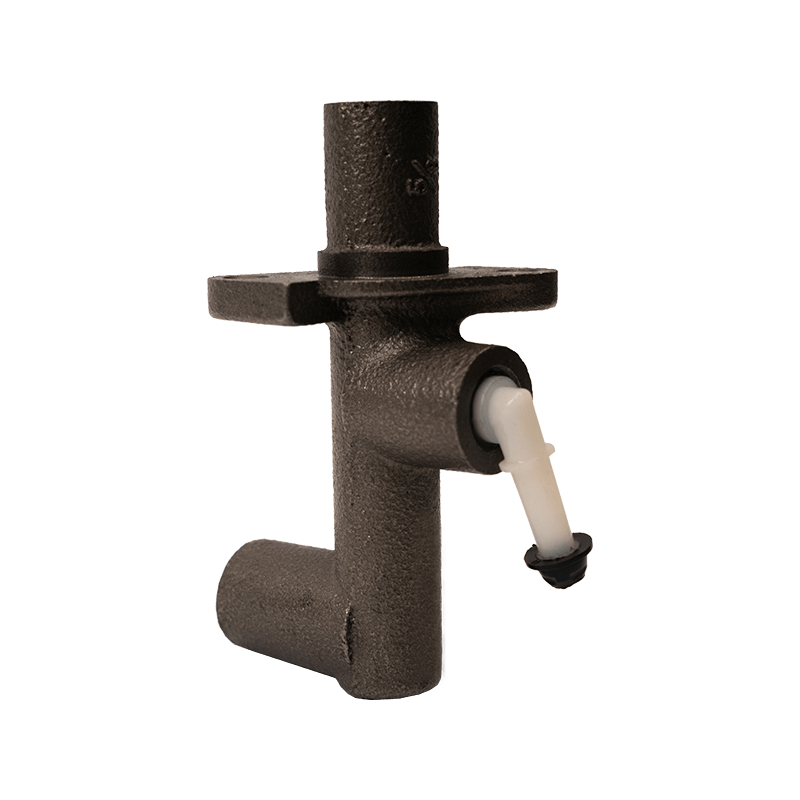
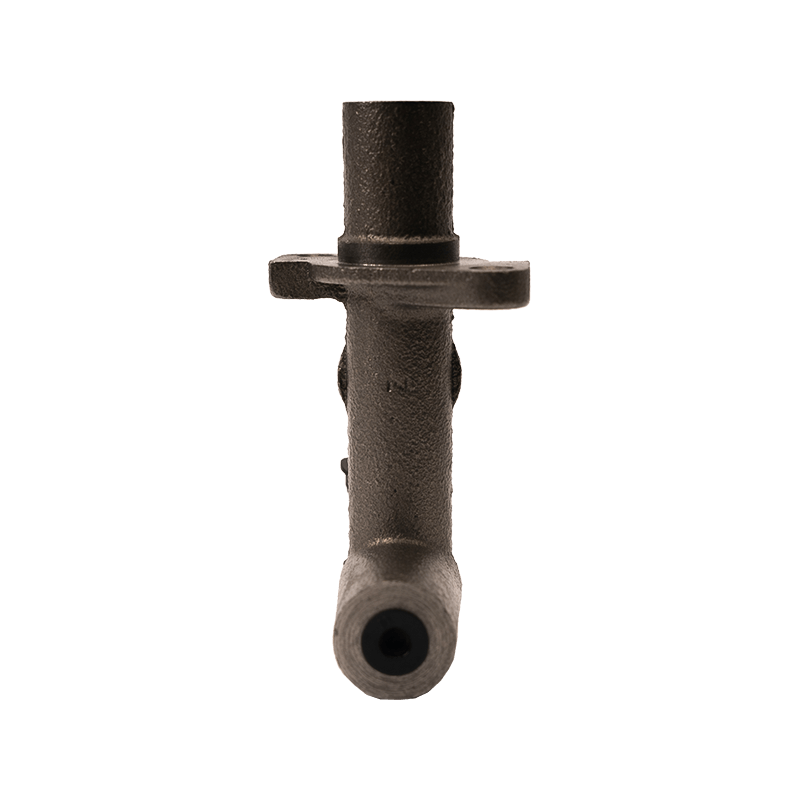
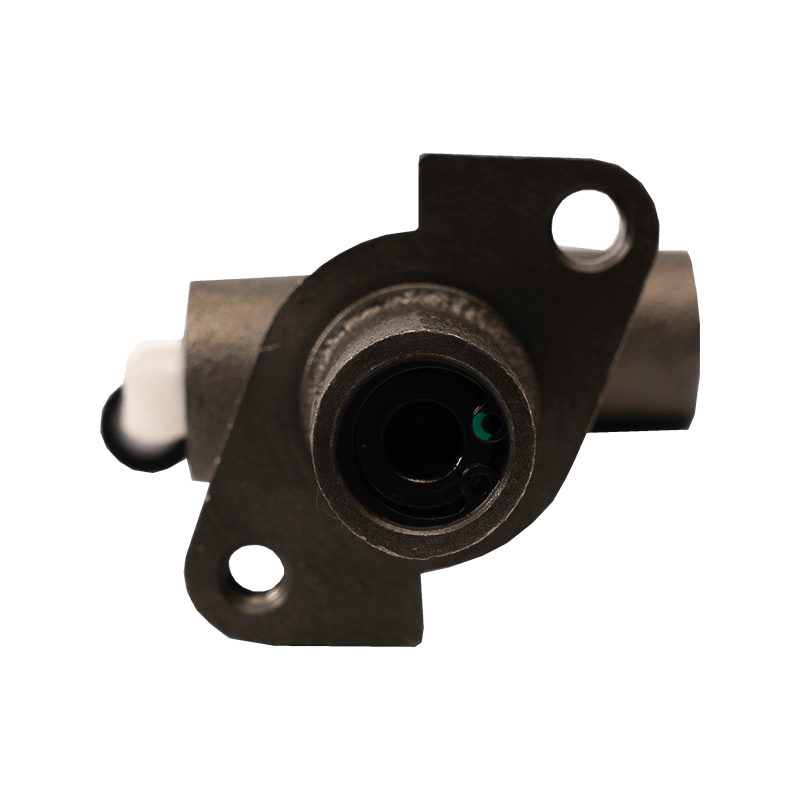
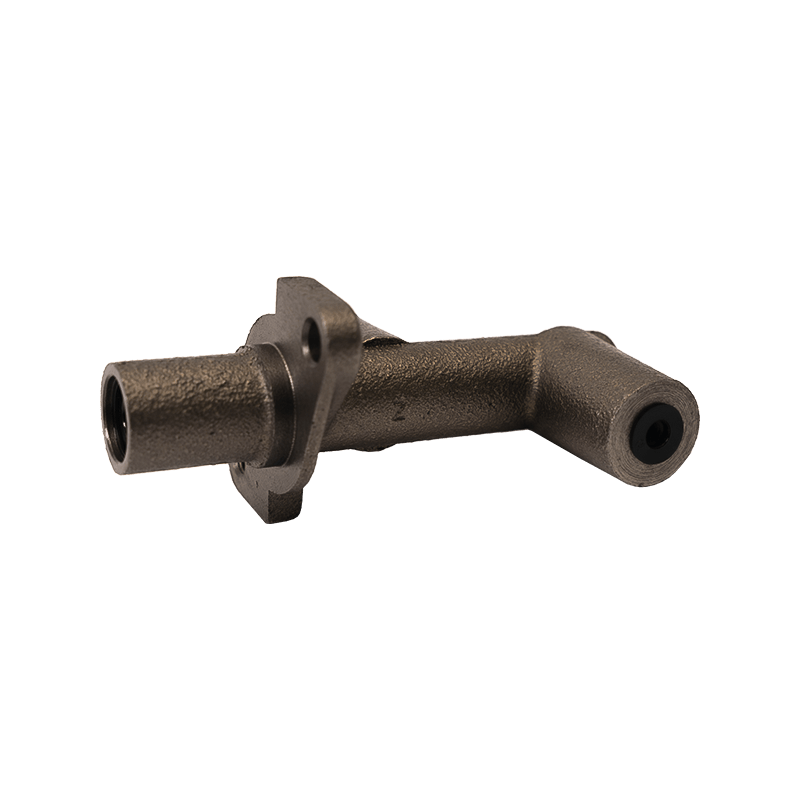
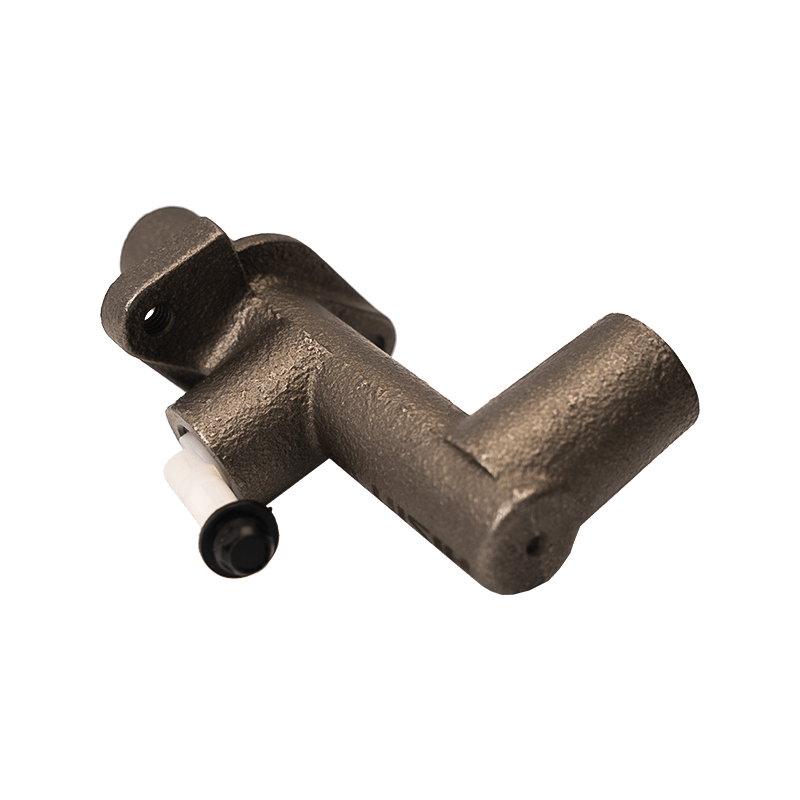
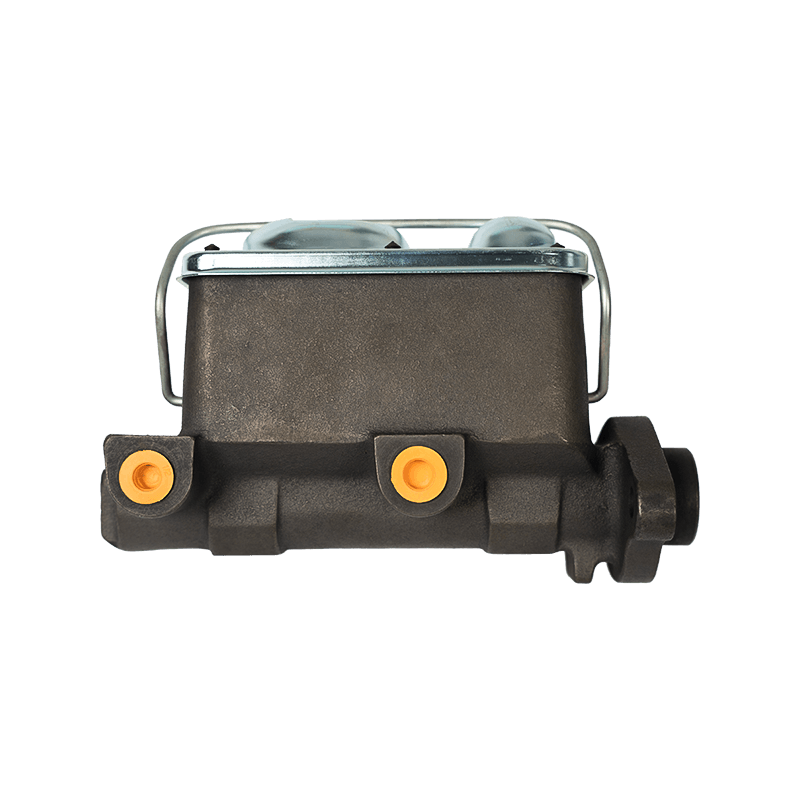
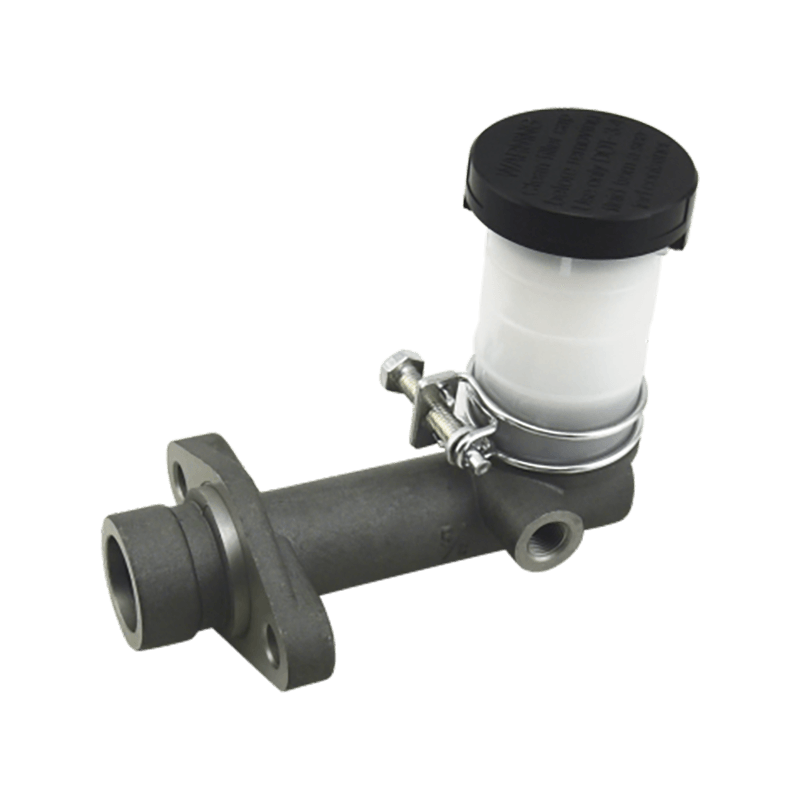
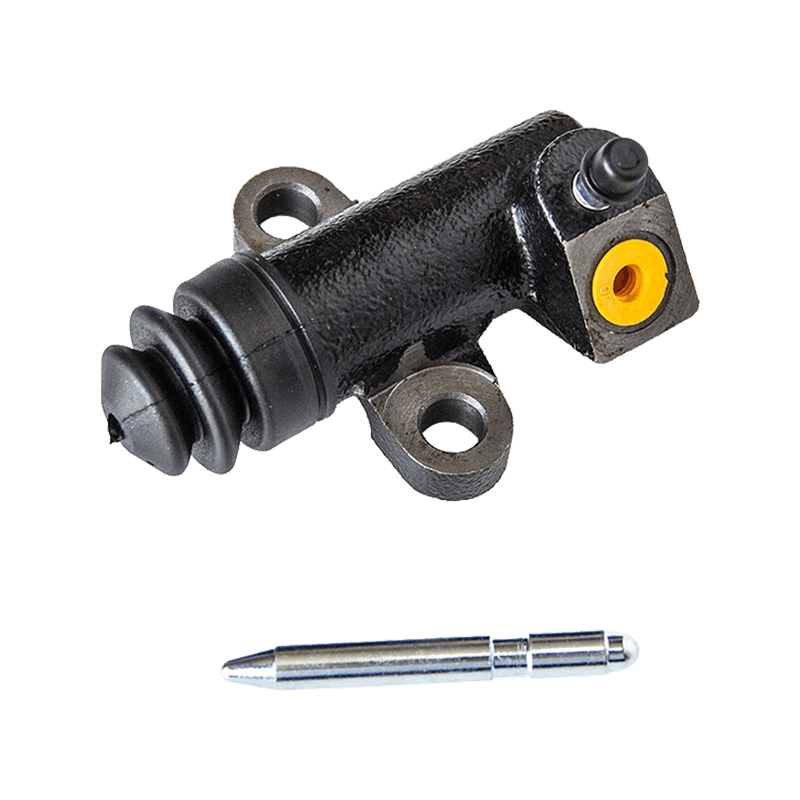
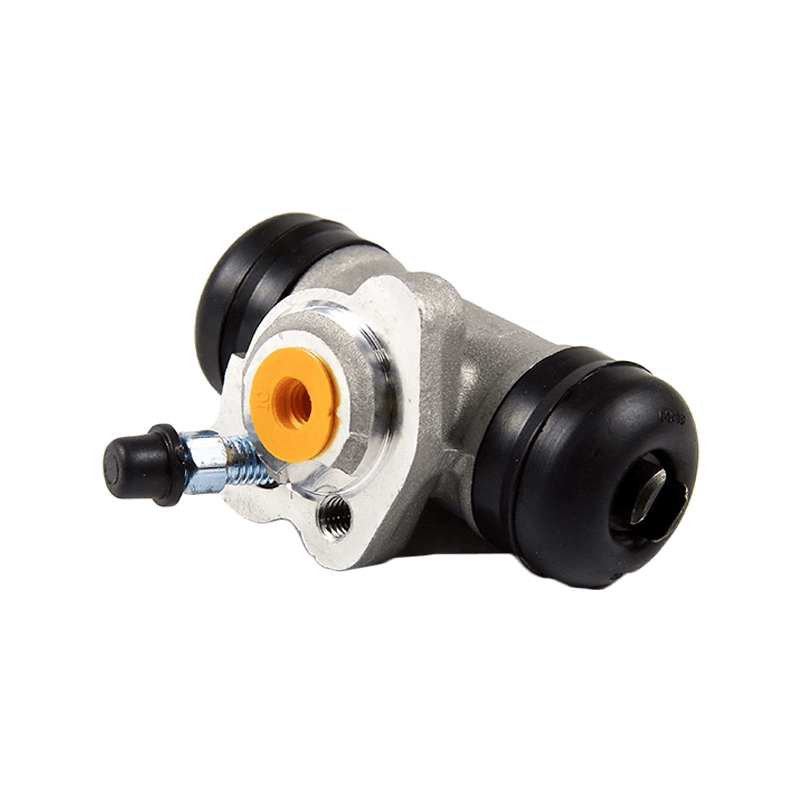
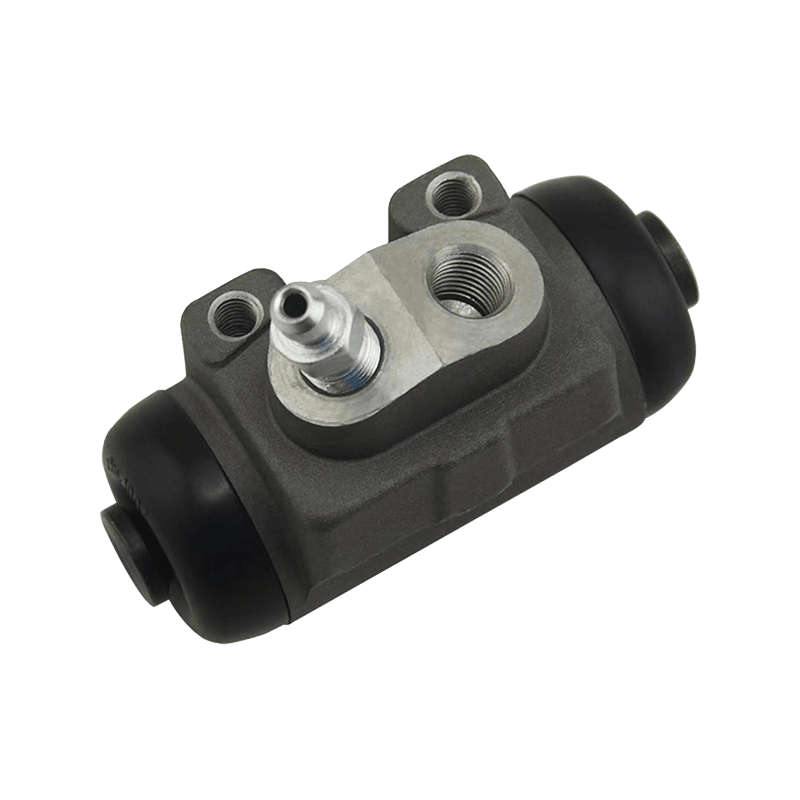
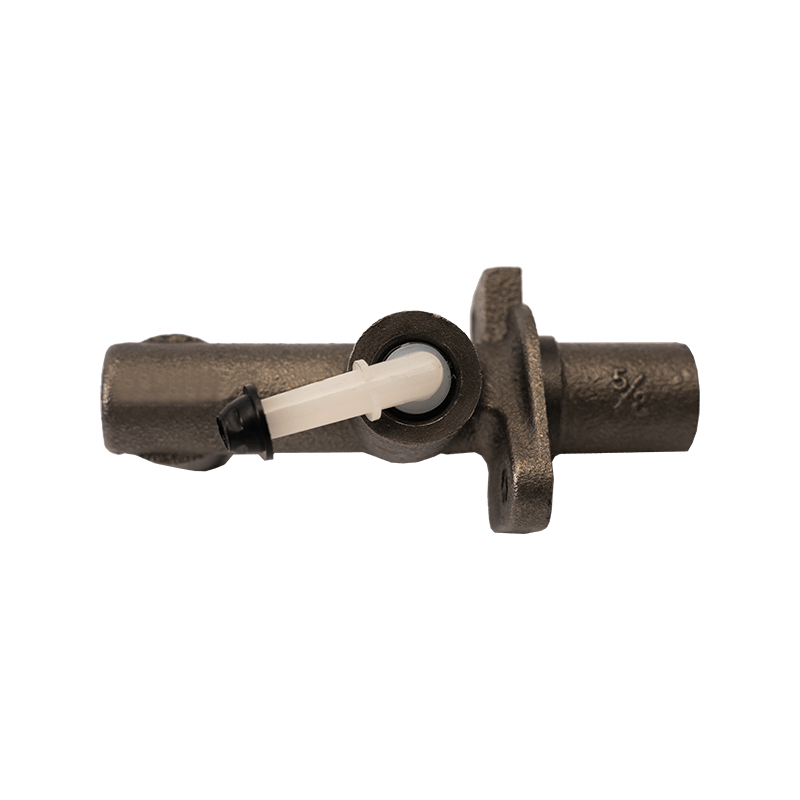
As the core actuator of the hydraulic clutch system, the BR7041990 Mazda clutch master cylinder converts the mechanical force input by the pedal into hydraulic thrust, accurately controls the separation and engagement of the clutch plate, and is especially suitable for the MX-3 (EC chassis), 323 C IV (BG chassis) and 323 F IV (BG chassis) produced between 1991 and 2000, covering a variety of engine versions from 1.6L to 1.8L.
The BR7041990 Clutch Master Cylinder For Mazda adopts a single piston structure design, and the piston seal is made of high-temperature resistant fluororubber. The temperature range covers -40℃ to 180℃, which can cope with high-frequency semi-clutch operation under congested urban road conditions. Its guide pin system has been nitrided and hardened, and with the double-layer dust cover design, it can effectively block more than 85% of the intrusion of mud and sand, reducing the risk of guide pin jamming. In response to environmental protection needs, some suppliers provide aluminum alloy versions, which are 28% lighter than the cast iron standard version.
If the vehicle has increased clutch pedal clearance, difficulty in shifting gears, or hydraulic leakage, it is recommended to check the master cylinder sealing system first. During installation, the torque specification must be strictly followed, and the bubbles must be completely removed by the two-stage pressure evacuation method. The DOT4 standard brake fluid must be replaced simultaneously to ensure hydraulic transmission efficiency. Insufficient lubrication of the shift fork may cause abnormal noise, and high-temperature resistant lithium-based grease must be applied regularly to avoid incomplete separation due to increased friction resistance.
 Search
Search
 Eng
Eng 
 English
English Español
Español Português
Português