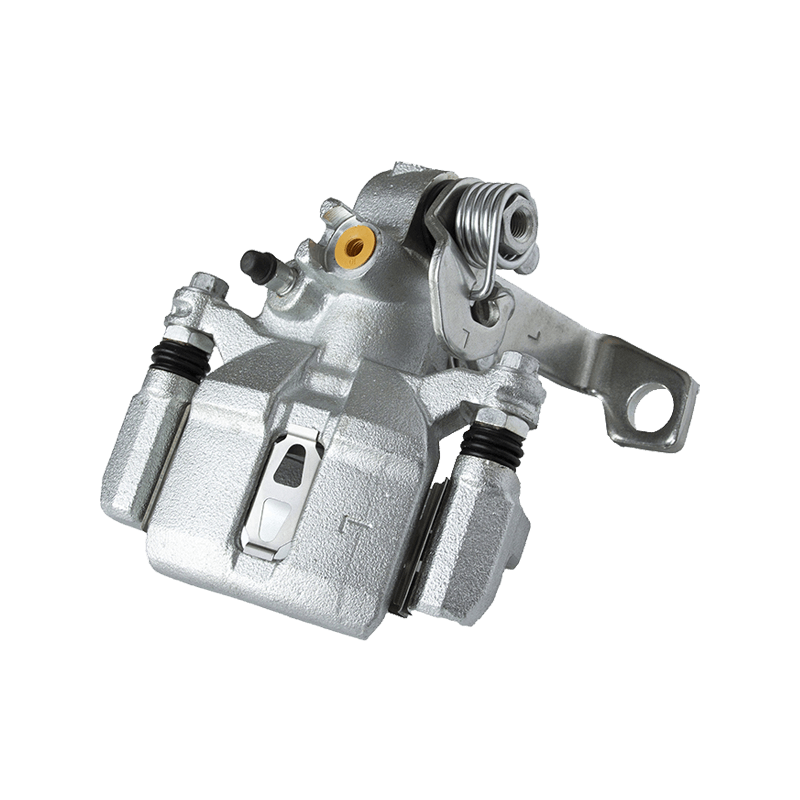
Fault diagnosis and solutions for abnormal noise and sticking of brake calipers
 2025.07.15
2025.07.15
 Industry News
Industry News
Content
1. Common causes and solutions for abnormal noise of brake calipers
Brake pad metal hard point friction
Phenomenon: A sharp and harsh metal friction sound is emitted when the brake is lightly pressed.
Cause: The brake pad contains metal particles or impurities, which directly rub against the brake disc.
Solution:
Step on the brake several times hard to try to grind off the hard points.
Remove the brake pad and grind the surface, or replace it with a high-quality brake pad (such as ceramic/low metal).
Improper assembly of brake pads
Phenomenon: Regular "clicking" sound when braking.
Cause: The brake pad is not installed correctly, such as reverse installation, insufficient lubrication or detachment of the retaining ring.
Solution:
Reinstall the brake pad and ensure the correct direction (wear indicator facing outward).
Apply high-temperature grease (such as copper-based grease) to the contact surface between the back of the brake pad and the caliper to reduce vibration noise.
Wear or poor lubrication of the guide pin
Phenomenon: Abnormal noise when braking at low speed, accompanied by loose brake pedal feel.
Cause: The guide pin is rusted or lacks lubrication, resulting in poor return of the brake pad.
Solution:
Remove the guide pin, clean the rust with fine sandpaper, and apply special silicone grease.
If the guide pin gap is too large (measured by a vernier caliper exceeding 0.1mm), a new pin needs to be replaced.
Deformation or wear of the brake disc
Phenomenon: The steering wheel shakes when braking, accompanied by periodic abnormal noise.
Cause: The brake disc is deformed due to high temperature or the surface groove is too deep.
Solution:
Minor deformation can be processed by disc (turning to repair flatness).
If the groove depth exceeds 1.5mm, the brake disc needs to be replaced, and the brake pad needs to be replaced simultaneously.

2. Diagnosis and repair of brake caliper jamming
Piston rust or sealing ring aging
Phenomenon: Wheel drag, increased fuel consumption, abnormal wear of brake pads (inner side wear).
Cause: The piston is stuck due to water or dirt, or the sealing ring loses elasticity.
Solution:
Remove the brake caliper, clean the piston with a rust remover, and manually press to test whether the return is smooth.
Replace the piston seal and add new brake fluid.
The brake caliper bolts are loose or improperly installed
Phenomenon: The abnormal sound is accompanied by a metal impact sound when braking, and the vehicle may deviate.
Cause: The caliper fixing bolts are not tightened or the bracket is deformed.
Solution:
Use a torque wrench to tighten the bolts according to the standard.
Check whether the bracket is deformed and replace it if necessary.
Brake fluid contamination or pipeline blockage
Phenomenon: The brake pedal returns slowly and the caliper is seriously heated.
Cause: The water content of the brake fluid exceeds the standard (more than 3%) or impurities in the pipeline hinder hydraulic transmission.
Solution:
Completely replace the brake fluid and clean the oil circuit.
Check whether the master cylinder is leaking and replace it if necessary.
3. Preventive maintenance recommendations
- Regular lubrication: Lubricate the guide pin and the brake pad contact point every 2 years or 30,000 kilometers.
- Brake fluid replacement: Check the water content every 2 years and replace it immediately if it exceeds the standard.
- Note in high temperature environment: Avoid frequent emergency braking to prevent the brake disc from overheating and deformation.
- Protection in rainy season: After wading, lightly press the brakes to evaporate water and reduce the risk of piston rust.
 Search
Search
 Eng
Eng 
 English
English Español
Español Português
Português