Why Choose OE Quality Brake Pads? When selecting brake pads, OE QUALITY BRAKE PADS ensure precise fit, optimal braking performance, and long-term durability. Unlike generic pads, OE pads are engineered to meet the origi...
READ MORE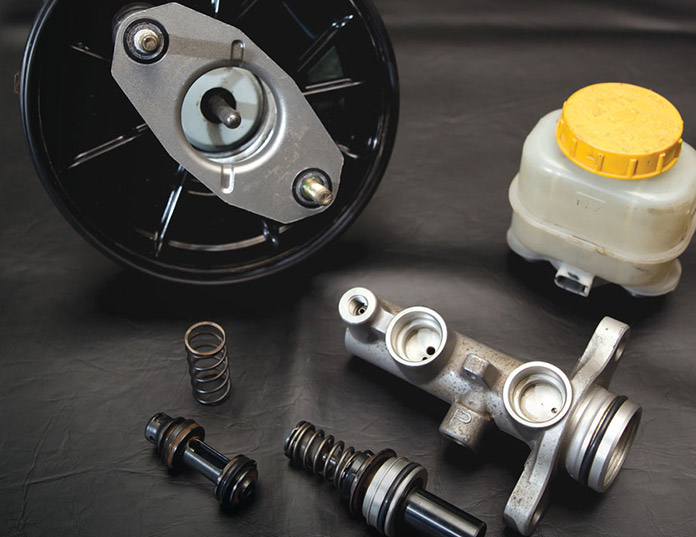
We have more than 1,000 brake shoes and brake pads for European, American, Russian, Japanese and Korean cars. The associated factories have created a highly experienced manufacturing team that exports thousands of auto part products worldwide. High quality and competitive prices are our targets. Our products have gained the certifications of ISO9001 and TS16949. We have built up a solid reputation with our customers in more than 30 countries.
We are looking forward to having a brighter and more successful business in the near future together with all of our clients all over the world.
-
-
What is a Hydraulic Brake Master Cylinder? The hydraulic brake master cylinder is a critical component in a vehicle's braking system. It converts the force applied to the brake pedal into hydraulic pressure, which is th...
READ MORE -
Why OE Quality Brake Pads Are the Best Choice for Your Car OE (Original Equipment) quality brake pads are specifically designed to match the specifications and performance standards set by the vehicle manufacturer. They...
READ MORE
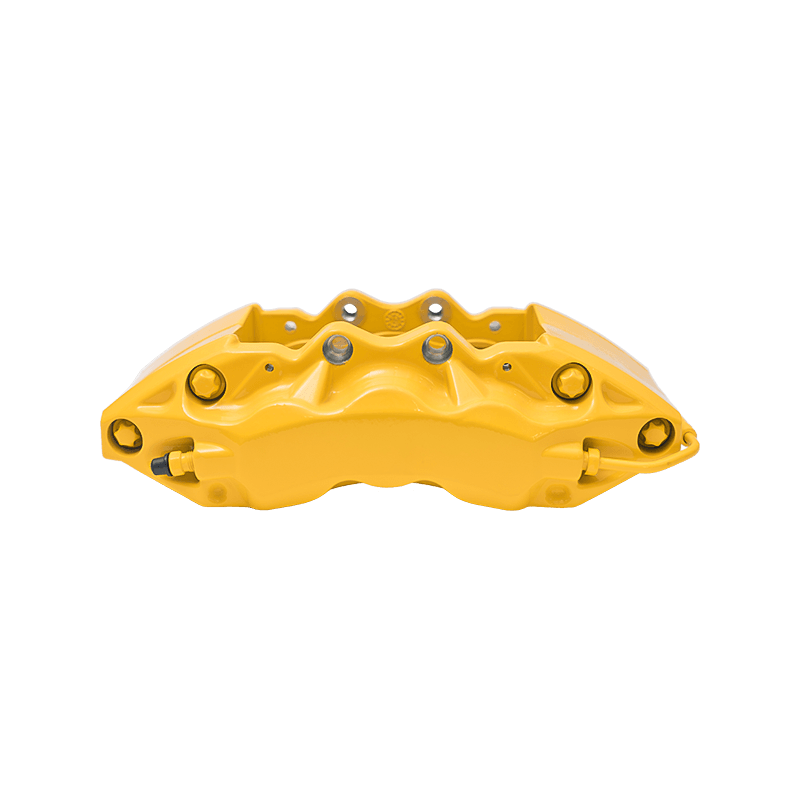
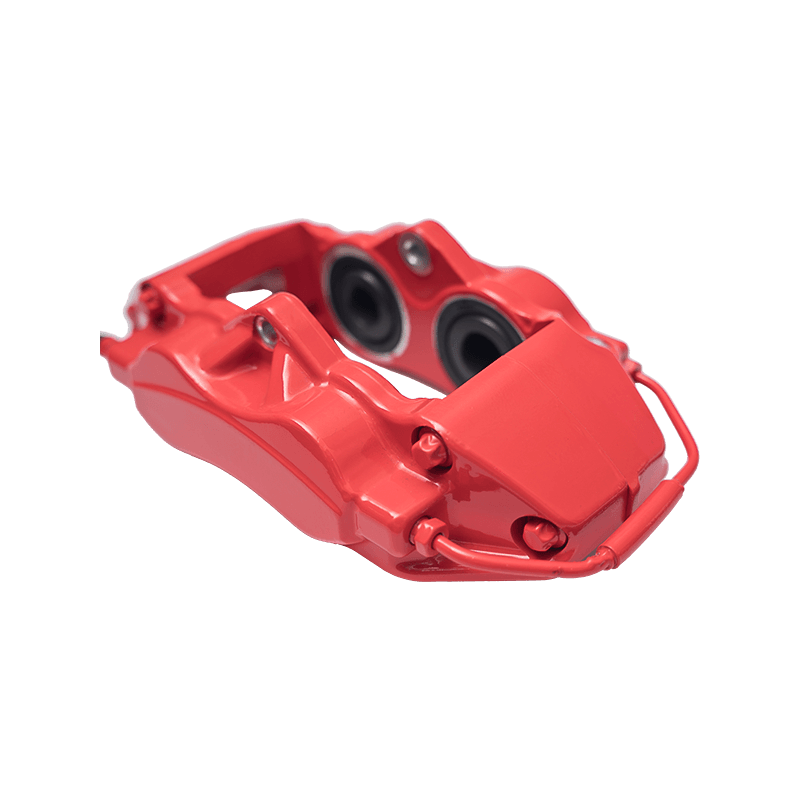
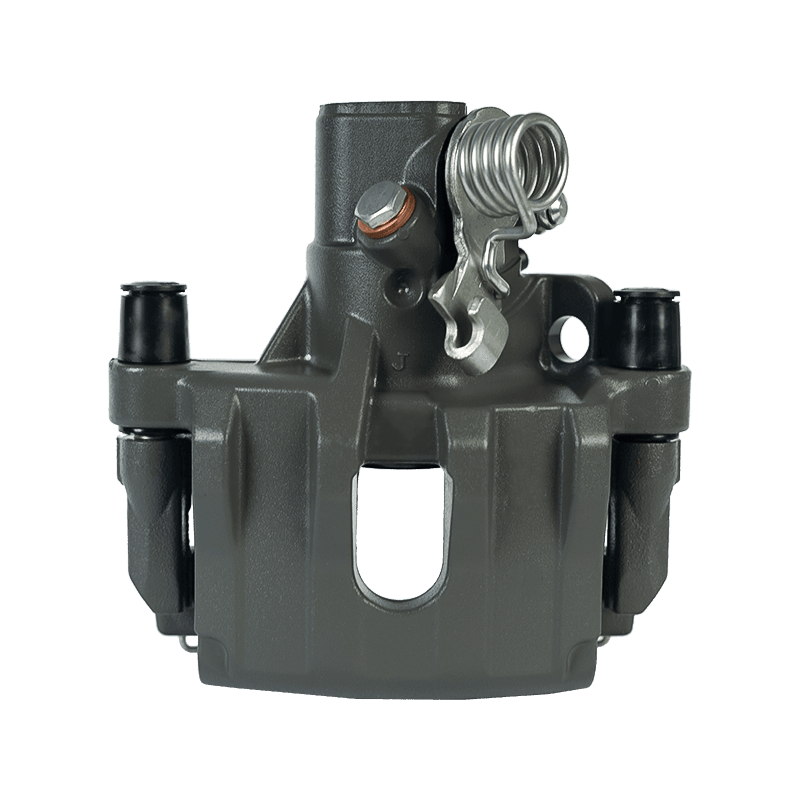
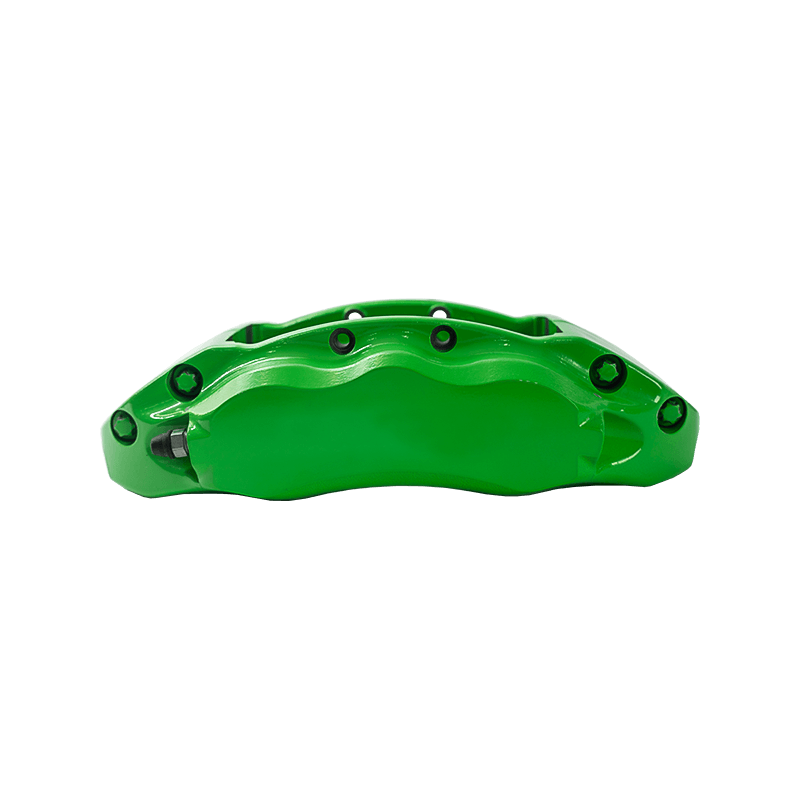
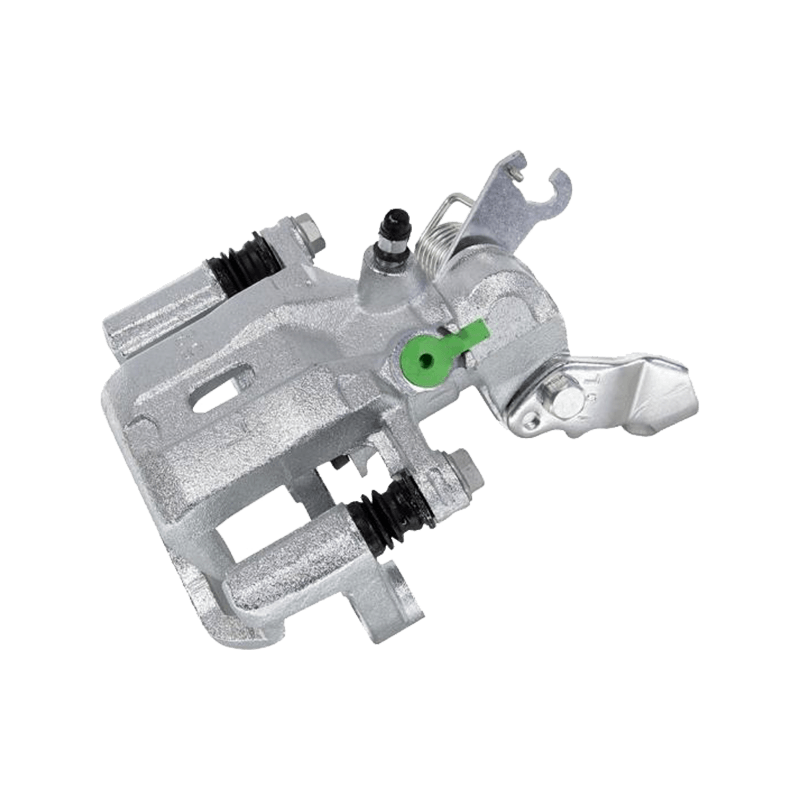
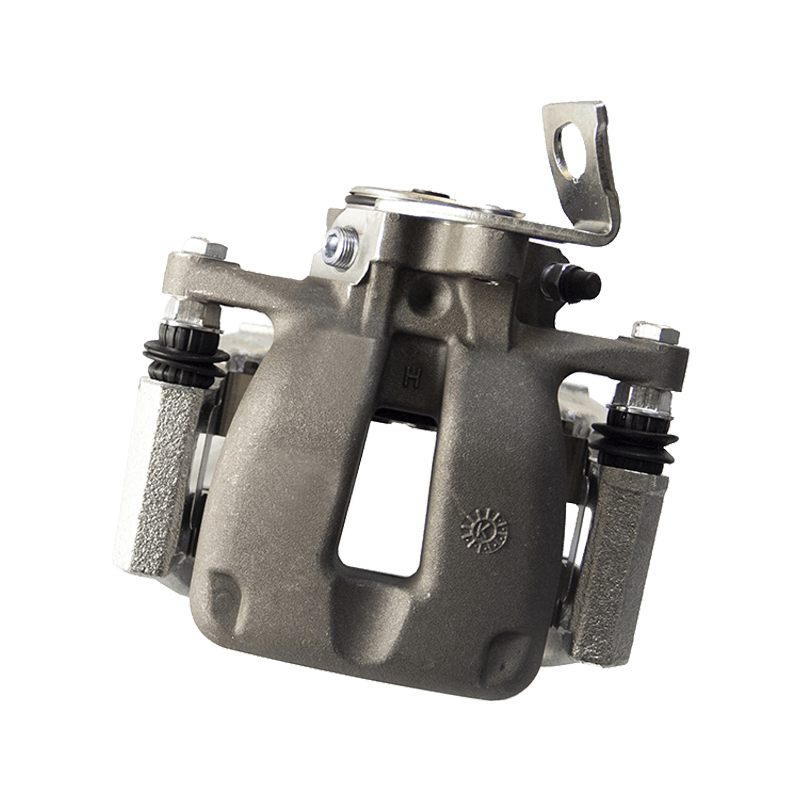
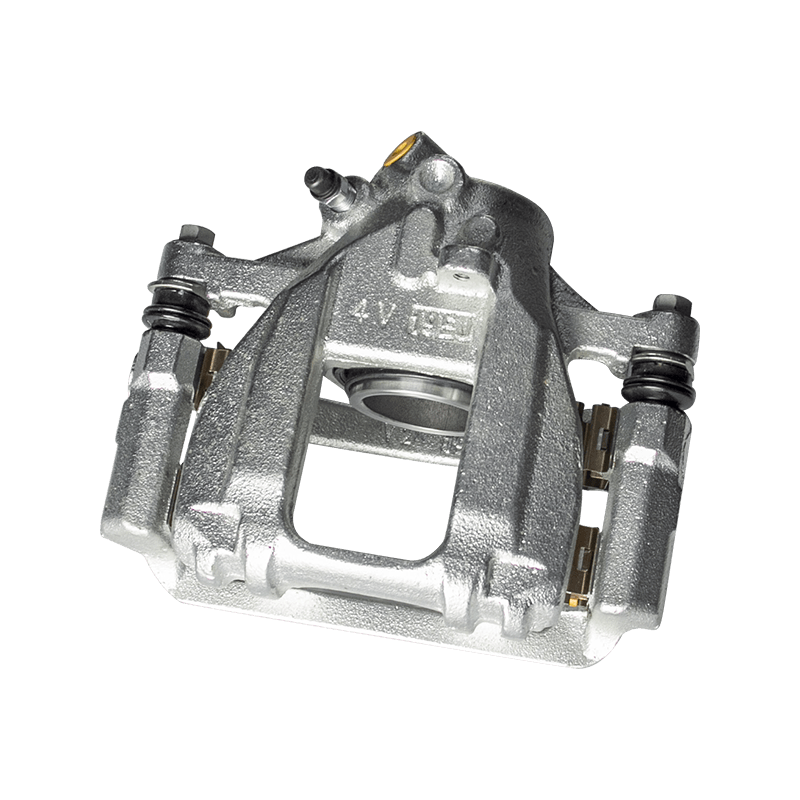
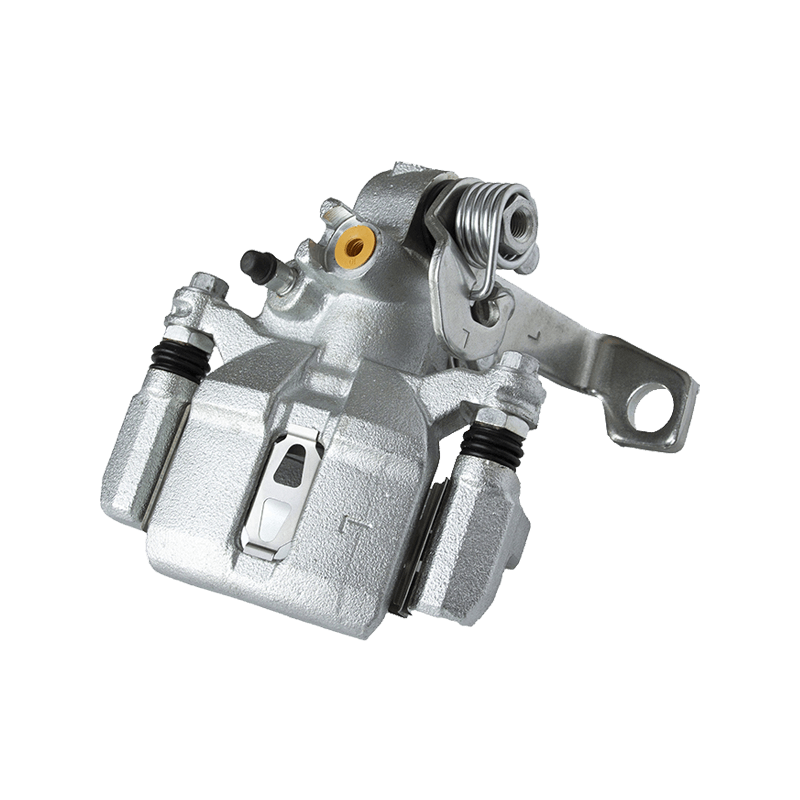
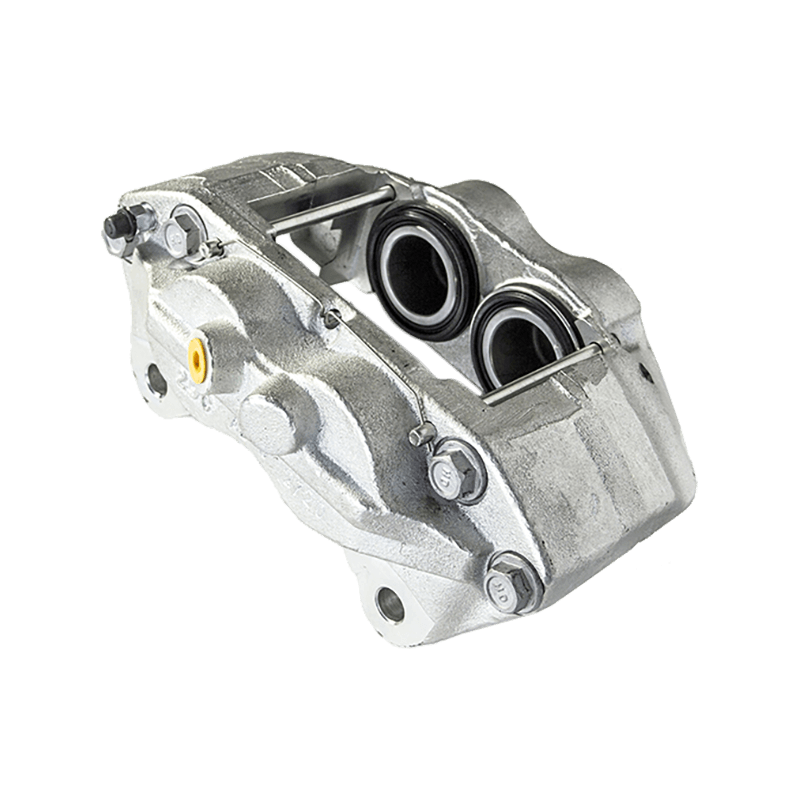
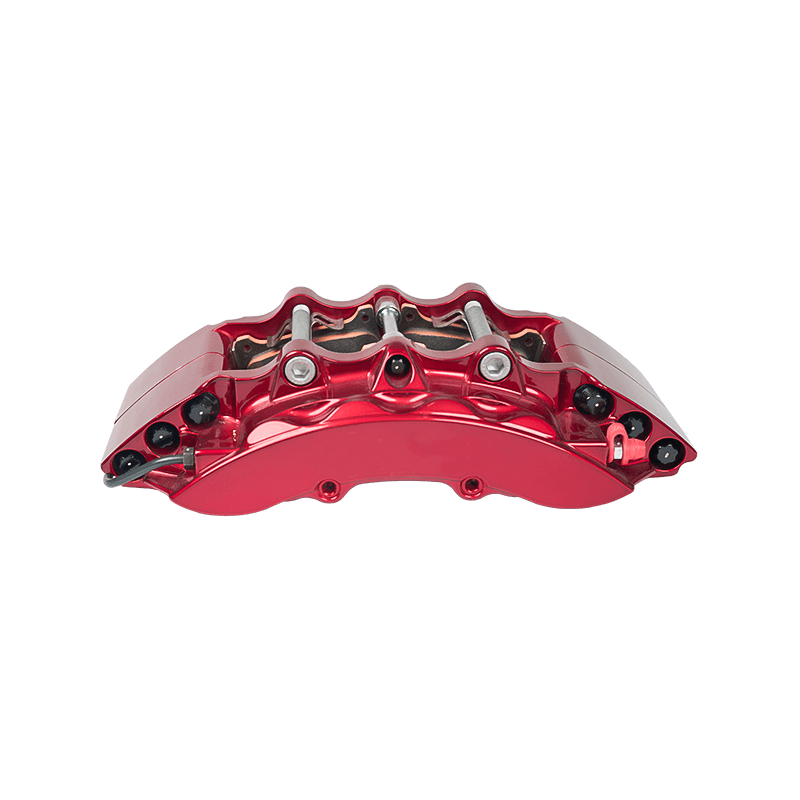
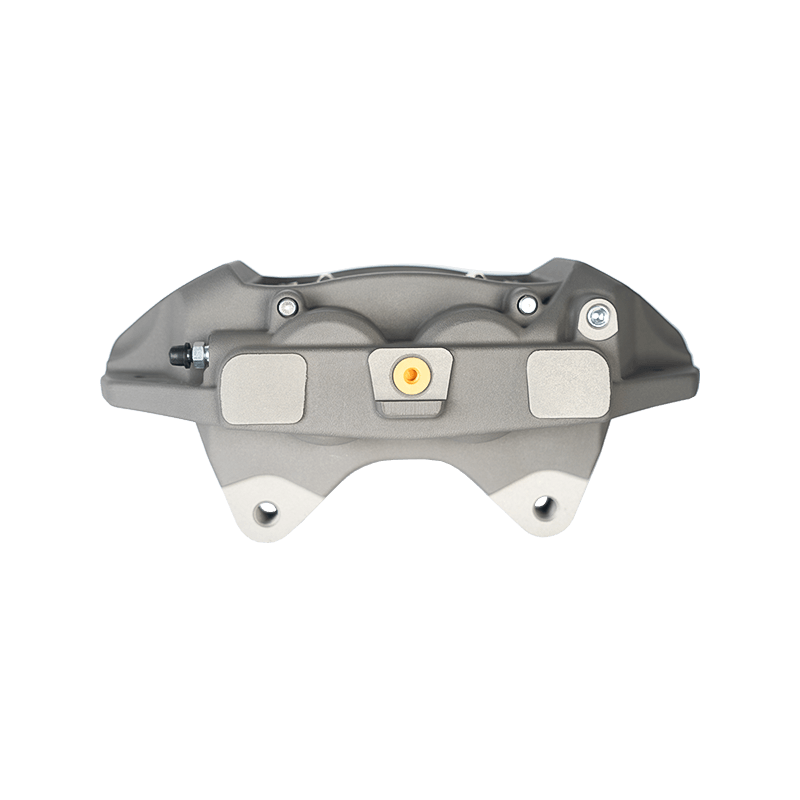
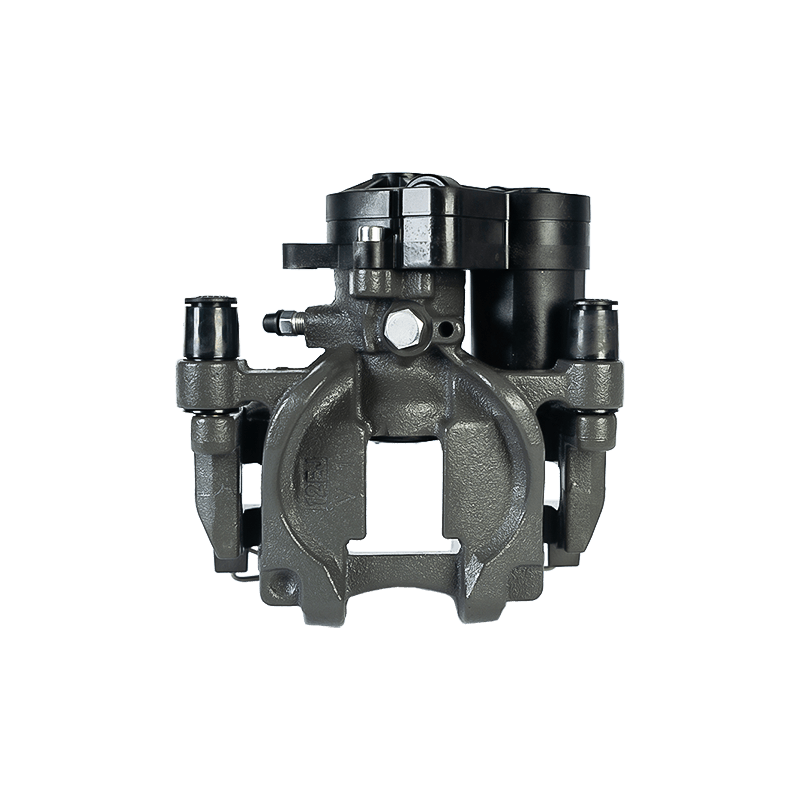
As the actuator of the disc brake system, the brake caliper is used to clamp the brake disc by hydraulically driving the friction pad, converting kinetic energy into heat energy to achieve vehicle deceleration. Brake calipers are mainly divided into two types: floating and fixed. The design differences directly affect the braking performance and applicable scenarios. The floating brake caliper pushes the inner friction pad to contact the brake disc through a single-sided piston. The reaction force causes the caliper body to slide along the guide pin, driving the outer friction pad to clamp synchronously to form a braking torque. This structure is compact and lightweight, with low cost, but its single-point pressure characteristics may cause uneven wear of the friction pad. The fixed brake caliper adopts a symmetrical layout of double-sided pistons to directly apply balanced pressure, with higher braking stiffness, and can accurately control the distribution of braking force to adapt to high-intensity braking needs.
The brake caliper has a built-in sealing ring and spring system to automatically compensate for the gap after the friction pad is worn. When the brake is released, the hydraulic pressure drops, and the elastic deformation of the sealing ring pushes the piston back to restore the small gap (usually 0.1 mm) between the friction pad and the brake disc to prevent the drag caused by continuous friction. Some models are also equipped with mechanical or electronic self-adjusting devices to further improve response accuracy.
The brake caliper converts the driver's braking command into reliable braking force through the clever combination of hydraulic drive and mechanical structure. Its design takes into account efficiency, heat dissipation and durability, becoming a key link in ensuring the safety of the car.
 Search
Search
 Eng
Eng 
 English
English Español
Español Português
Português