Why Choose OE Quality Brake Pads? When selecting brake pads, OE QUALITY BRAKE PADS ensure precise fit, optimal braking performance, and long-term durability. Unlike generic pads, OE pads are engineered to meet the origi...
READ MORE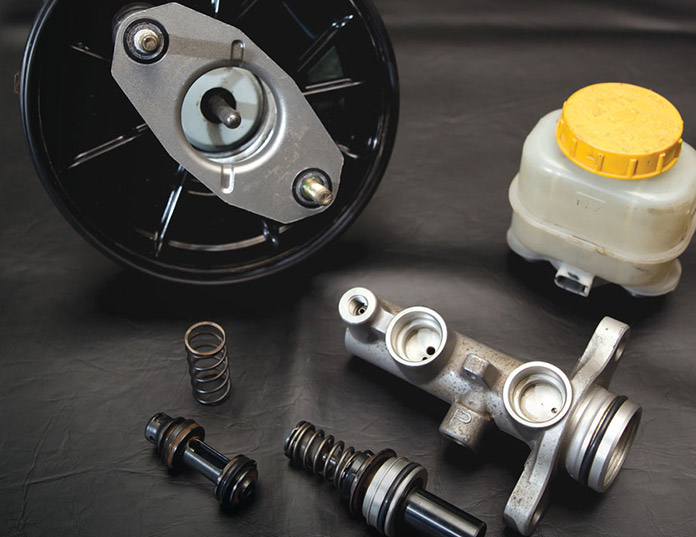
We have more than 1,000 brake shoes and brake pads for European, American, Russian, Japanese and Korean cars. The associated factories have created a highly experienced manufacturing team that exports thousands of auto part products worldwide. High quality and competitive prices are our targets. Our products have gained the certifications of ISO9001 and TS16949. We have built up a solid reputation with our customers in more than 30 countries.
We are looking forward to having a brighter and more successful business in the near future together with all of our clients all over the world.
-
-
What is a Hydraulic Brake Master Cylinder? The hydraulic brake master cylinder is a critical component in a vehicle's braking system. It converts the force applied to the brake pedal into hydraulic pressure, which is th...
READ MORE -
Why OE Quality Brake Pads Are the Best Choice for Your Car OE (Original Equipment) quality brake pads are specifically designed to match the specifications and performance standards set by the vehicle manufacturer. They...
READ MORE
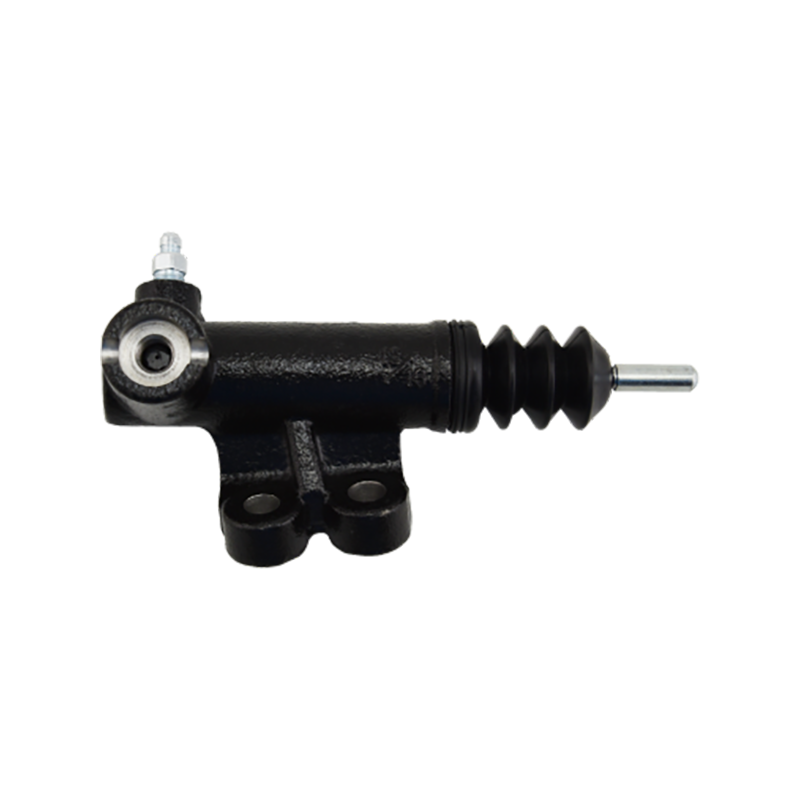
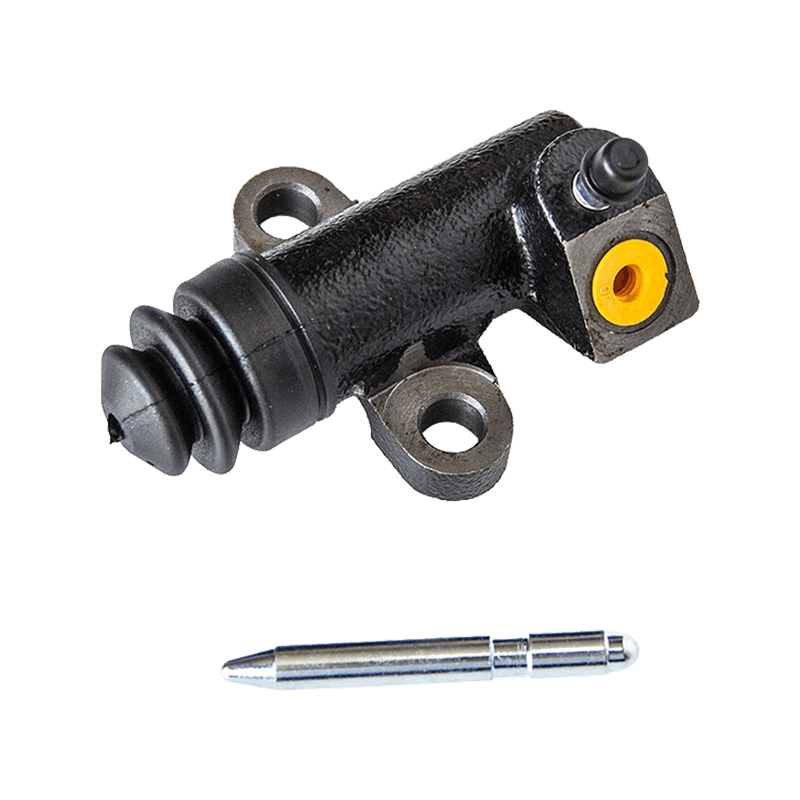
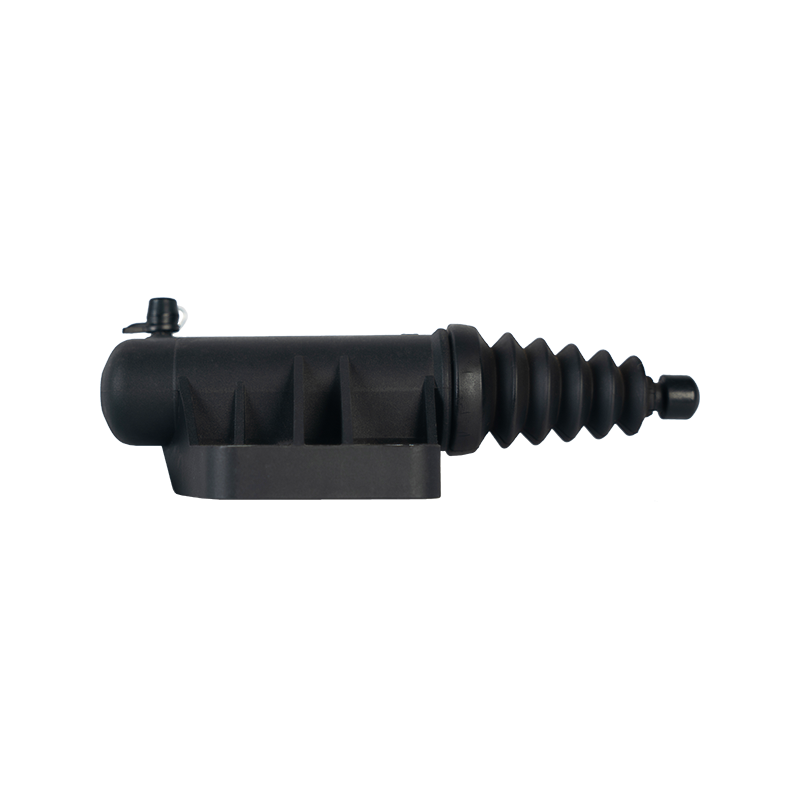
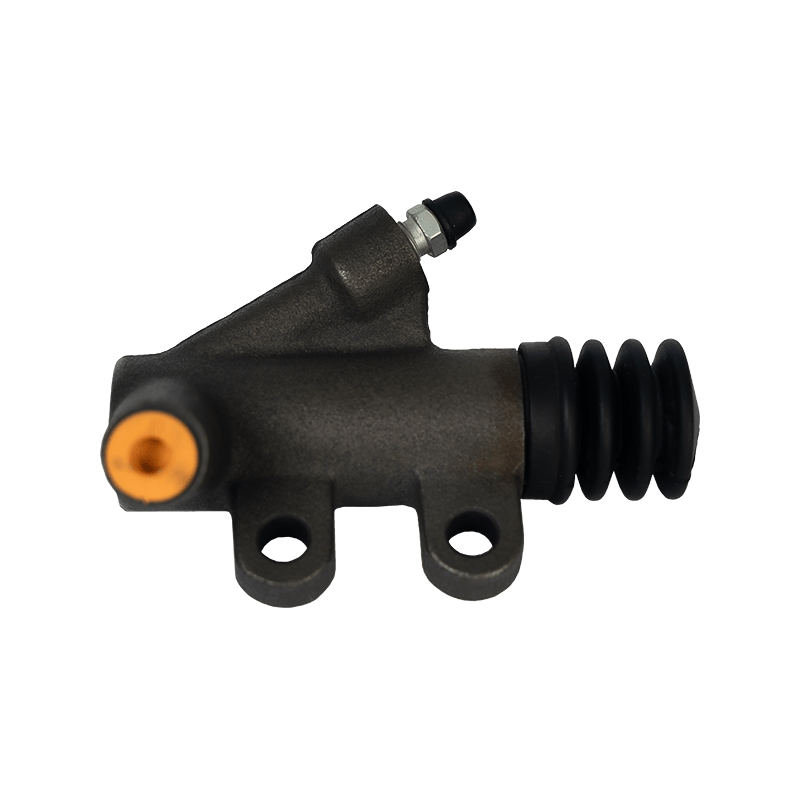
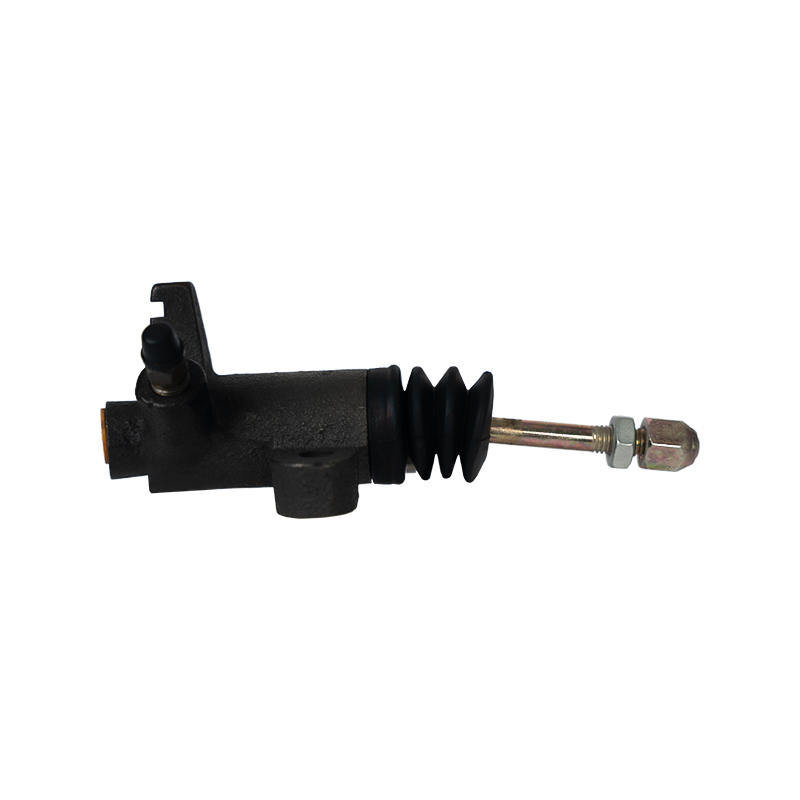
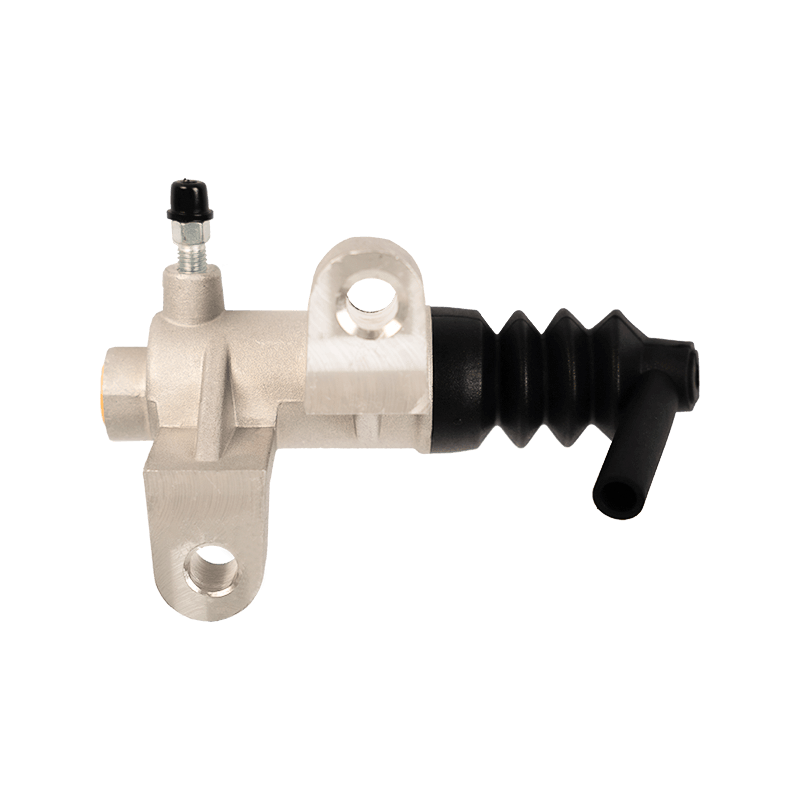
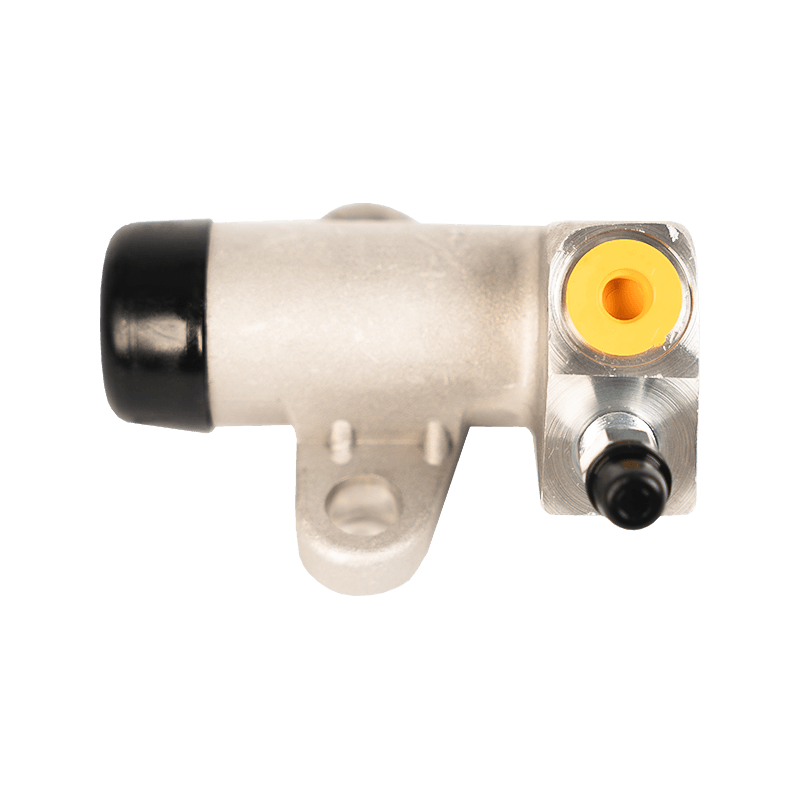
The clutch slave cylinder is an important actuator in the automobile hydraulic clutch system. When working, it converts the hydraulic energy transmitted by the main pump into the axial thrust of the release bearing, and finally moves the clutch pressure plate to release the engine power, completing the power connection and disconnection during the gear shifting process. When the driver steps on the clutch pedal, the hydraulic oil generated by the main pump is pressed into the slave cylinder cavity through the pipeline, pushing the internal piston and push rod to extend outward, forcing the release bearing to slide along the input shaft of the gearbox, and the pressure plate spring releases the clamping of the friction plate under the thrust of the bearing to achieve clutch separation. This process requires the slave cylinder to respond to the pedal action in a short time, and the thrust must accurately match the elastic coefficient of the pressure plate spring. Any hysteresis or force deviation will cause gear shifting frustration or clutch slippage.
The structural design of the slave cylinder takes into account both strength and lightweight requirements. It usually uses an aluminum alloy casting shell with a nylon composite piston, and the sealing ring uses high-temperature resistant fluororubber to ensure long-term anti-aging performance. In terms of spatial layout, the external slave pump is fixed to the gearbox housing through a bracket, and the push rod and the release rocker arm adopt a ball head hinge design, which allows a slight displacement compensation when the vehicle bumps; while the integrated slave pump is directly nested inside the gearbox release bearing to reduce the mechanical loss of the transmission link.
The reliability of the clutch slave pump is directly related to the sensitivity and durability of the clutch system. Leakage caused by aging of the seal ring is the most common fault, which manifests as the clutch pedal "softening" or abnormal increase in free travel. At this time, the hydraulic oil will seep out along the push rod seal and pollute the clutch housing. In special cases, piston jamming will cause the release bearing to continue to press the pressure plate, accelerate the wear of the friction plate and cause abnormal noise in the gearbox. During maintenance, special attention should be paid to exhausting the bubbles in the hydraulic pipeline-two people cooperate to repeatedly step on the clutch pedal until the brake fluid without bubbles flows out of the slave pump bleed valve, and then the system response speed can be restored. The modern slave pump has introduced a self-adjusting function, which compensates for the gap changes caused by the wear of the friction plate through the built-in spring, so that the clutch pedal stroke always maintains a linear foot feel.
 Search
Search
 Eng
Eng 
 English
English Español
Español Português
Português