Why Choose OE Quality Brake Pads? When selecting brake pads, OE QUALITY BRAKE PADS ensure precise fit, optimal braking performance, and long-term durability. Unlike generic pads, OE pads are engineered to meet the origi...
READ MORE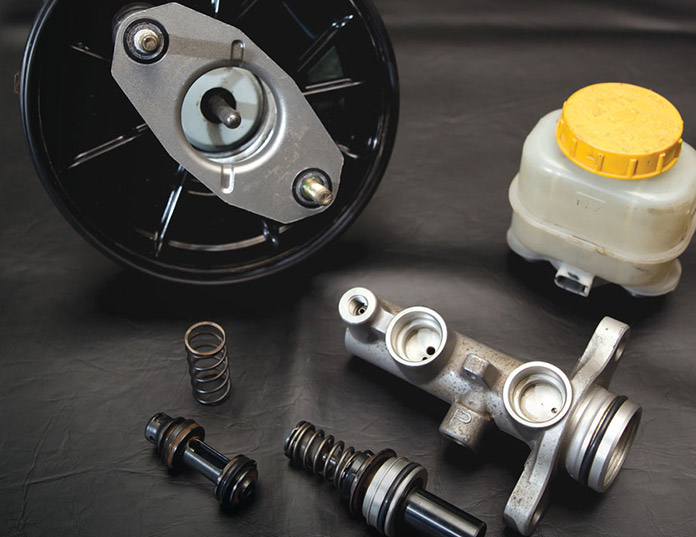
We have more than 1,000 brake shoes and brake pads for European, American, Russian, Japanese and Korean cars. The associated factories have created a highly experienced manufacturing team that exports thousands of auto part products worldwide. High quality and competitive prices are our targets. Our products have gained the certifications of ISO9001 and TS16949. We have built up a solid reputation with our customers in more than 30 countries.
We are looking forward to having a brighter and more successful business in the near future together with all of our clients all over the world.
-
-
What is a Hydraulic Brake Master Cylinder? The hydraulic brake master cylinder is a critical component in a vehicle's braking system. It converts the force applied to the brake pedal into hydraulic pressure, which is th...
READ MORE -
Why OE Quality Brake Pads Are the Best Choice for Your Car OE (Original Equipment) quality brake pads are specifically designed to match the specifications and performance standards set by the vehicle manufacturer. They...
READ MORE
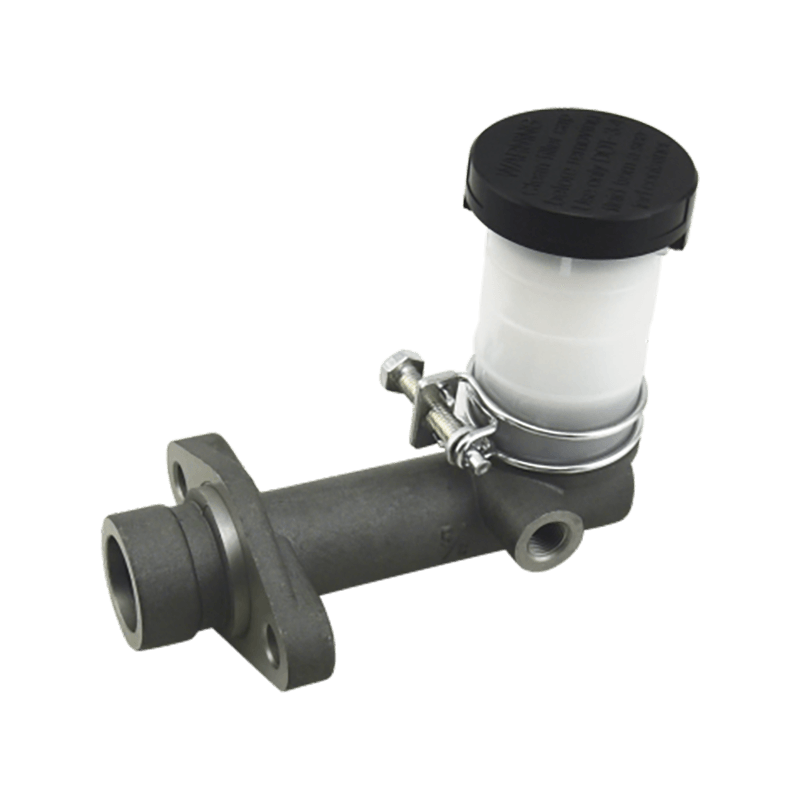
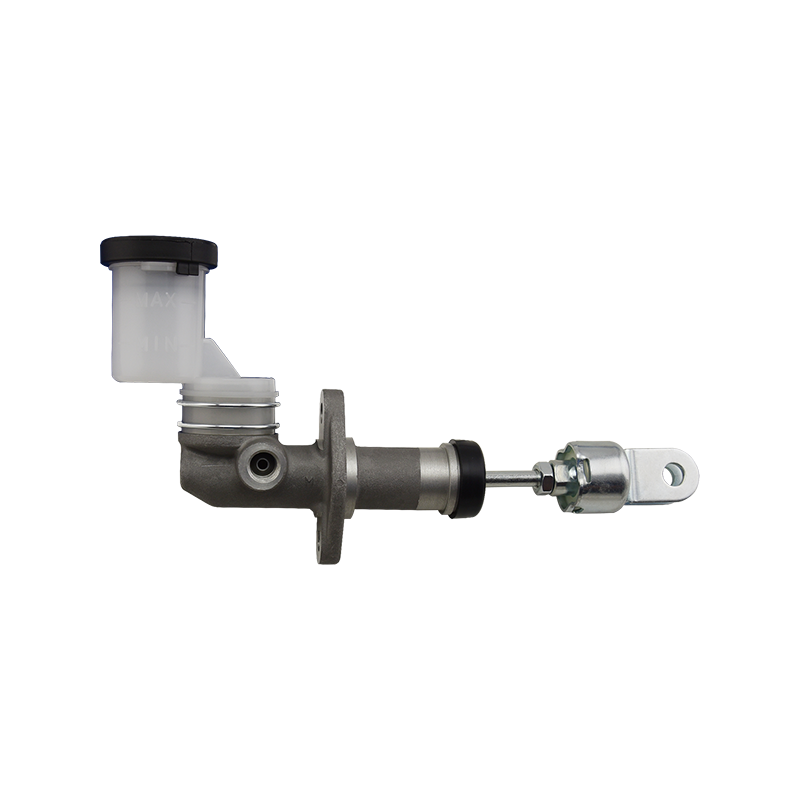
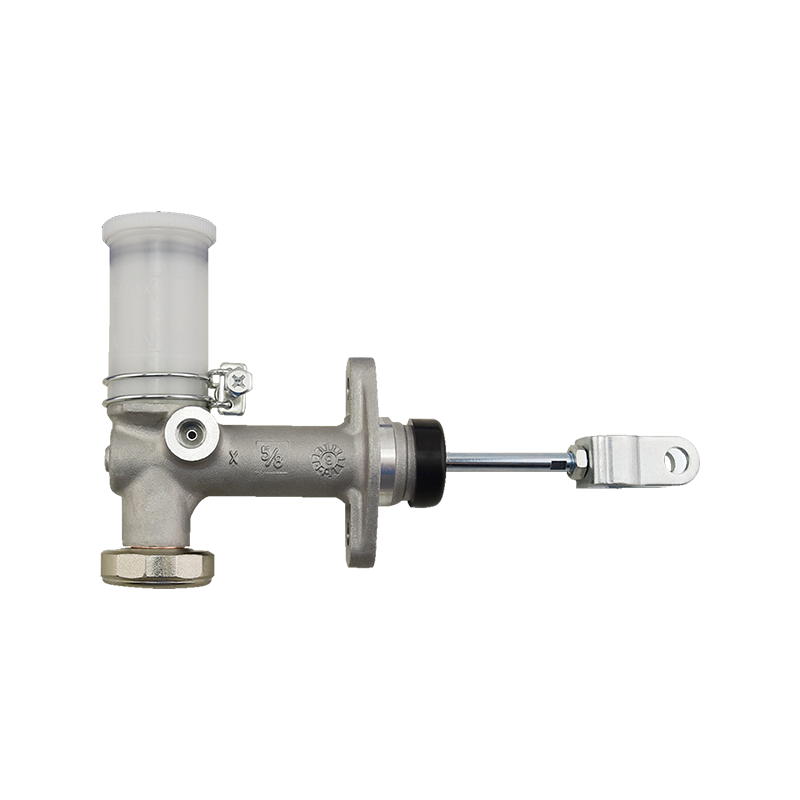
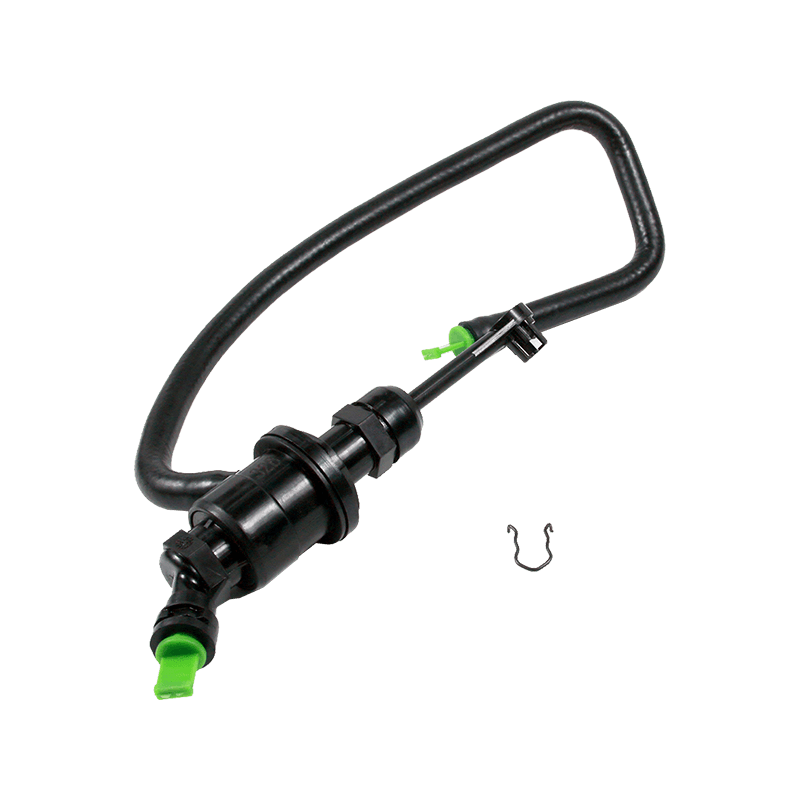
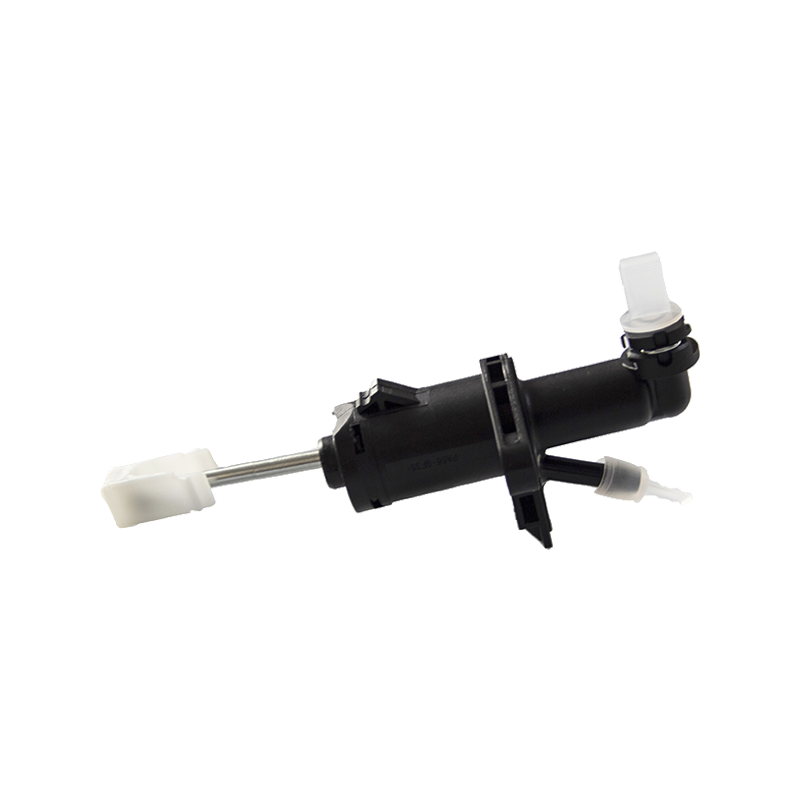
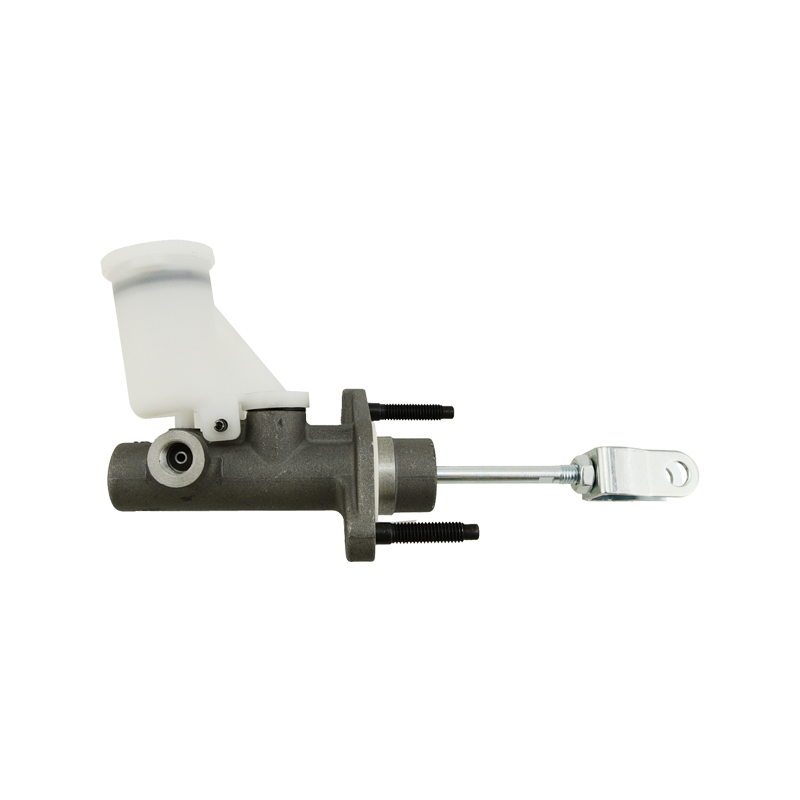
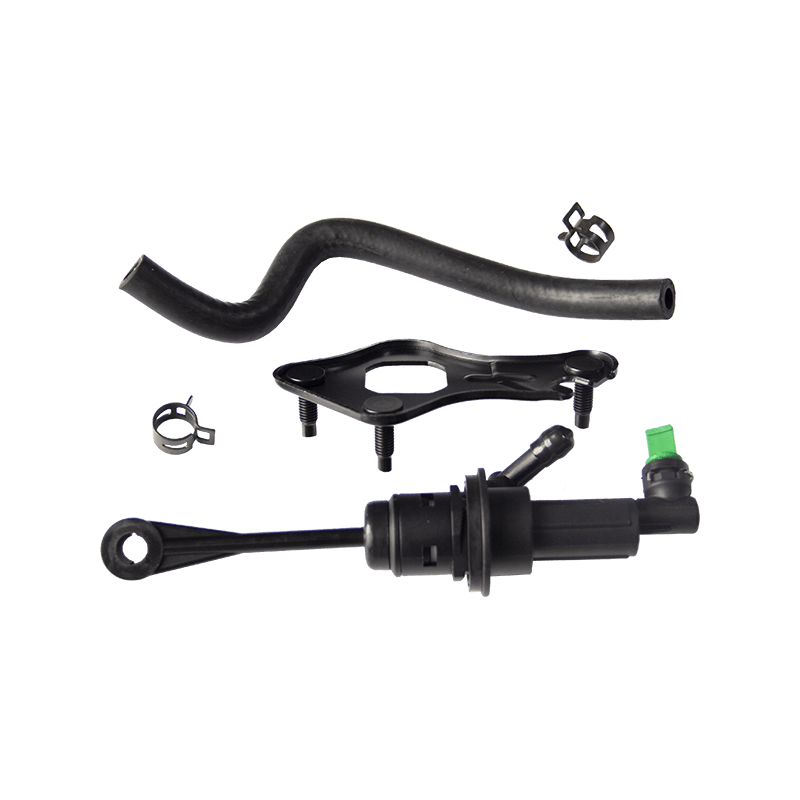
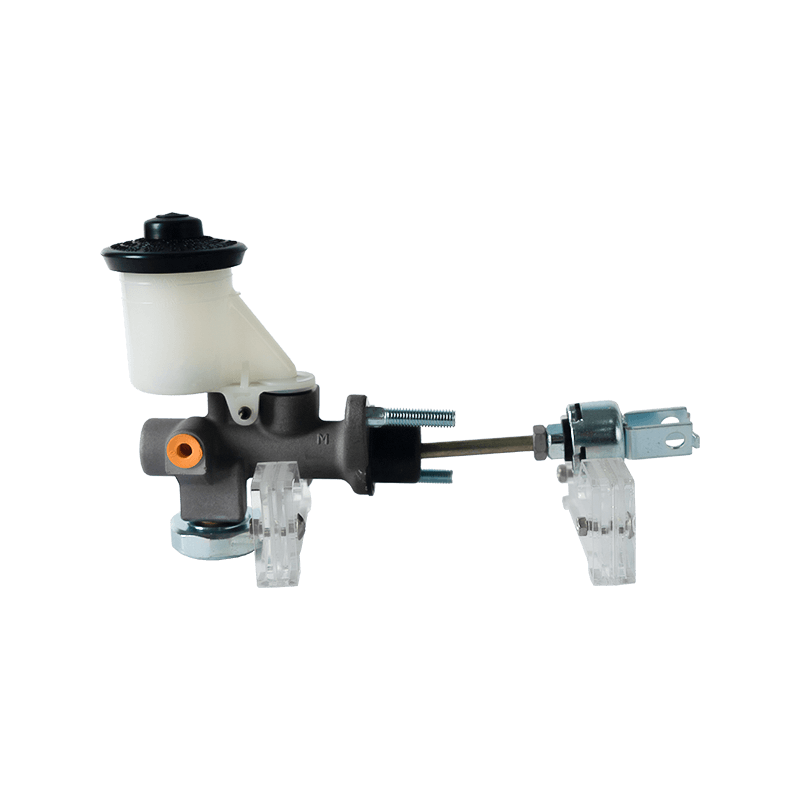
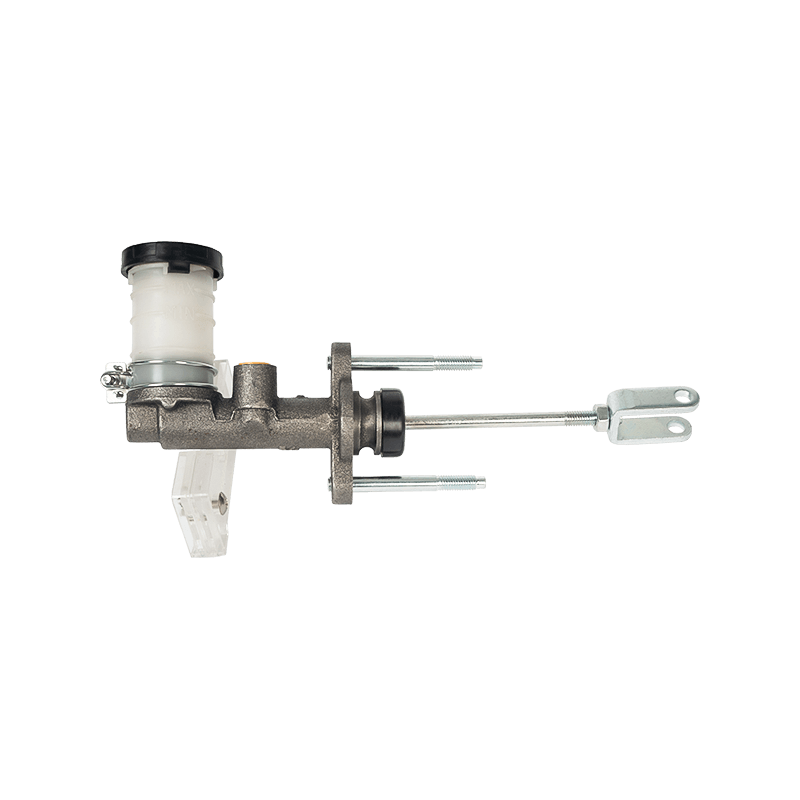
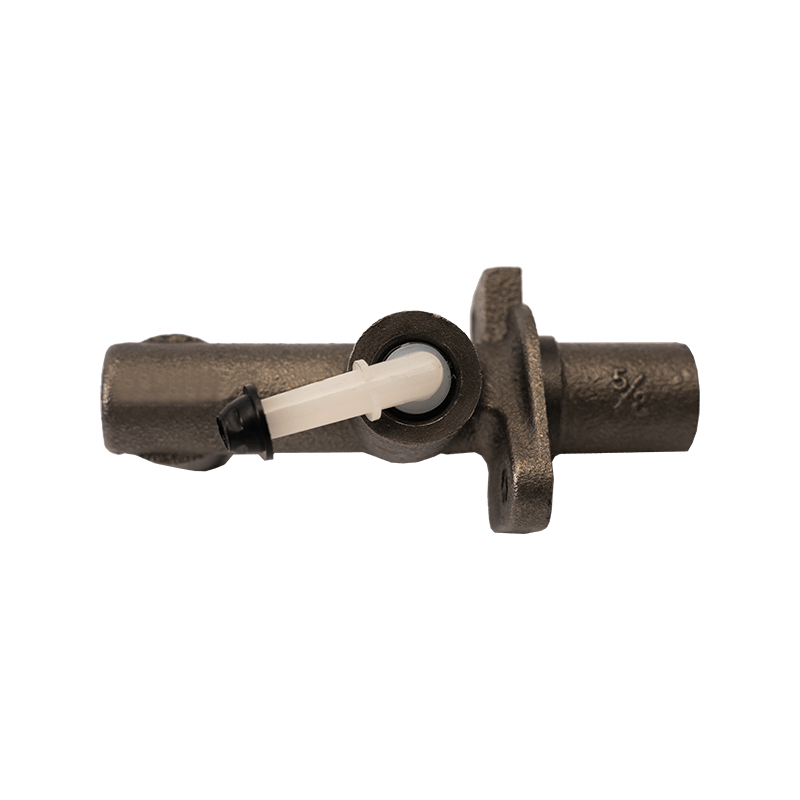
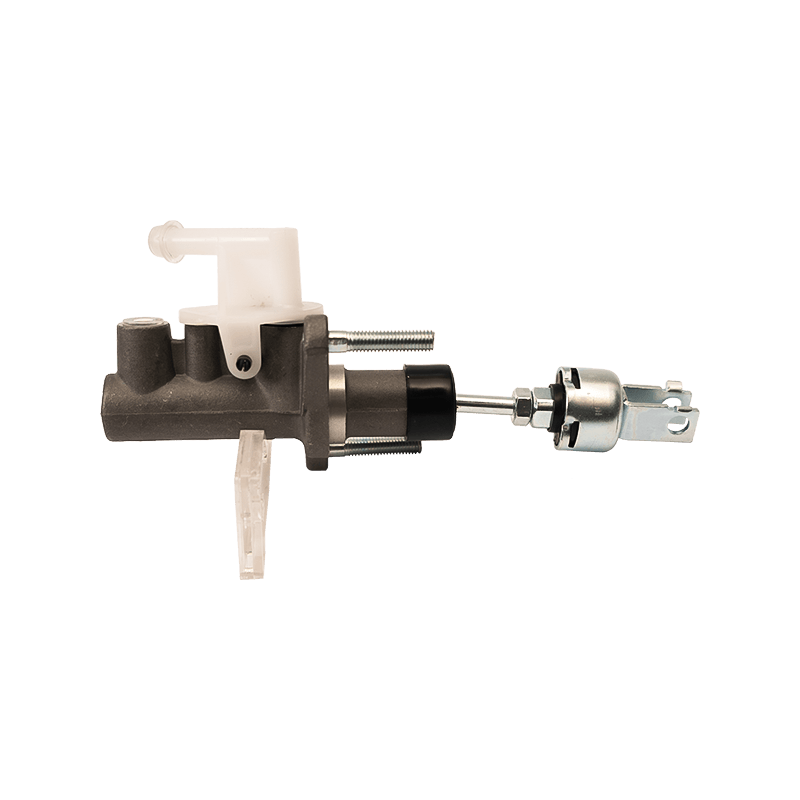
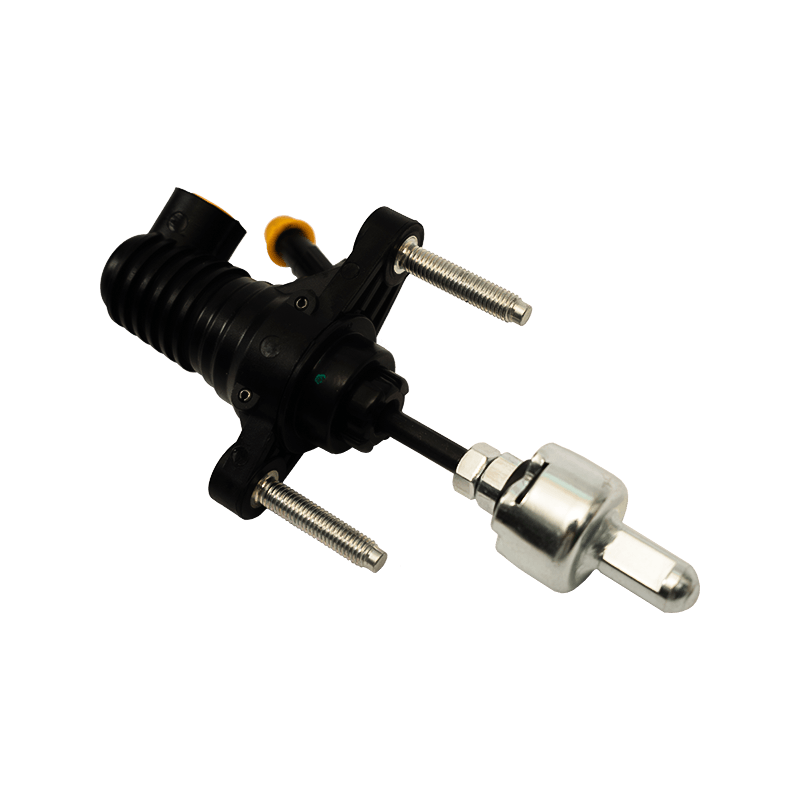
The clutch master cylinder is the core component of the clutch hydraulic system of a manual transmission car. It serves as a bridge between the driver's foot movement and the clutch actuator. It converts the mechanical force of the pedal into a hydraulic control signal to ensure that the engine power and the transmission system are smoothly connected or completely separated. When the driver steps on the clutch pedal, the push rod pushes the master cylinder piston to compress the brake oil in the reservoir, establishes high pressure in the closed pipeline, drives the clutch slave cylinder piston to move, and finally completes the clutch action by shifting the pressure plate through the release bearing. The millisecond response of this process determines the smoothness of gear shifting and the efficiency of power transmission.
The clutch master cylinder is mostly made of aluminum alloy casting shell with steel piston, and the internal precision-designed compensation hole and oil inlet valve form a dynamic balance system. The compensation hole replenishes oil when the pedal returns to its position to avoid bubbles in the hydraulic pipeline; the oil inlet valve ensures that there is no "empty stroke" when the clutch is stepped on quickly. With the advancement of technology, the integrated master pump has gradually replaced the split structure. Some models have integrated the reservoir and the pump body to reduce the risk of leakage while reducing the installation space requirements.
The stability of the clutch master pump directly affects the driving experience. When the internal seal ring ages or the piston wears, the pedal feel becomes softer and the stroke virtual position increases. In severe cases, the clutch cannot be completely separated, and it is difficult to shift gears or the gearbox makes abnormal noises. When driving in a low-temperature environment, the increased viscosity of inferior hydraulic oil may cause the pedal to rebound slowly, exposing the error between the design of the master pump return valve and the fluidity of the oil. Pay special attention to the air exhaust operation during maintenance-two people cooperate to repeatedly step on the pedal until the oil without bubbles overflows from the slave pump to restore the sensitivity of the hydraulic system.
 Search
Search
 Eng
Eng 
 English
English Español
Español Português
Português