Why Choose OE Quality Brake Pads? When selecting brake pads, OE QUALITY BRAKE PADS ensure precise fit, optimal braking performance, and long-term durability. Unlike generic pads, OE pads are engineered to meet the origi...
READ MORE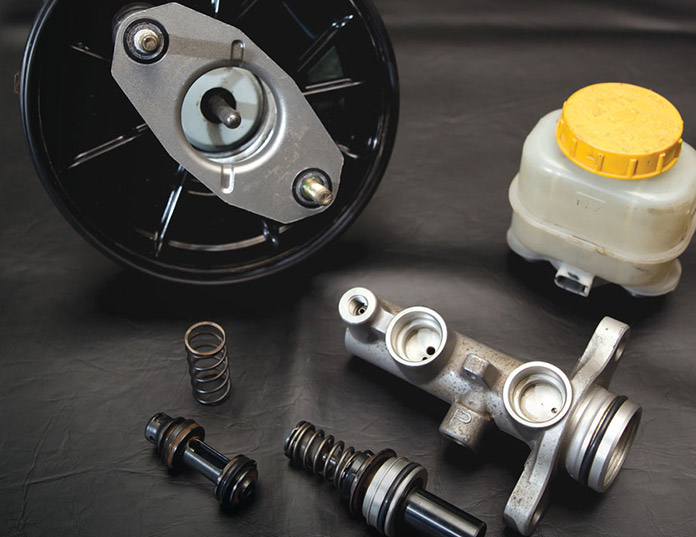
We have more than 1,000 brake shoes and brake pads for European, American, Russian, Japanese and Korean cars. The associated factories have created a highly experienced manufacturing team that exports thousands of auto part products worldwide. High quality and competitive prices are our targets. Our products have gained the certifications of ISO9001 and TS16949. We have built up a solid reputation with our customers in more than 30 countries.
We are looking forward to having a brighter and more successful business in the near future together with all of our clients all over the world.
-
-
What is a Hydraulic Brake Master Cylinder? The hydraulic brake master cylinder is a critical component in a vehicle's braking system. It converts the force applied to the brake pedal into hydraulic pressure, which is th...
READ MORE -
Why OE Quality Brake Pads Are the Best Choice for Your Car OE (Original Equipment) quality brake pads are specifically designed to match the specifications and performance standards set by the vehicle manufacturer. They...
READ MORE
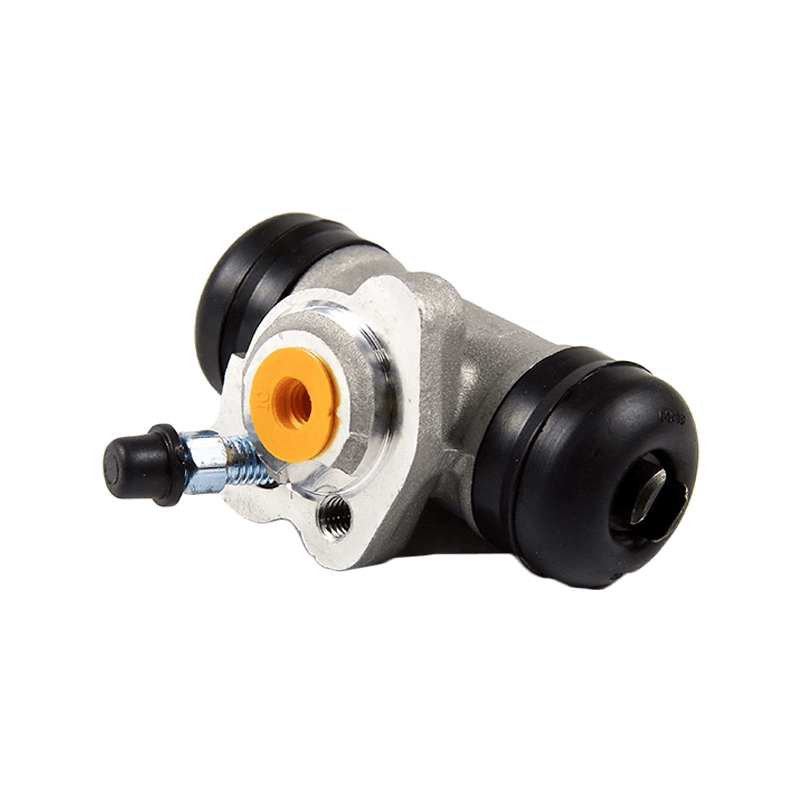
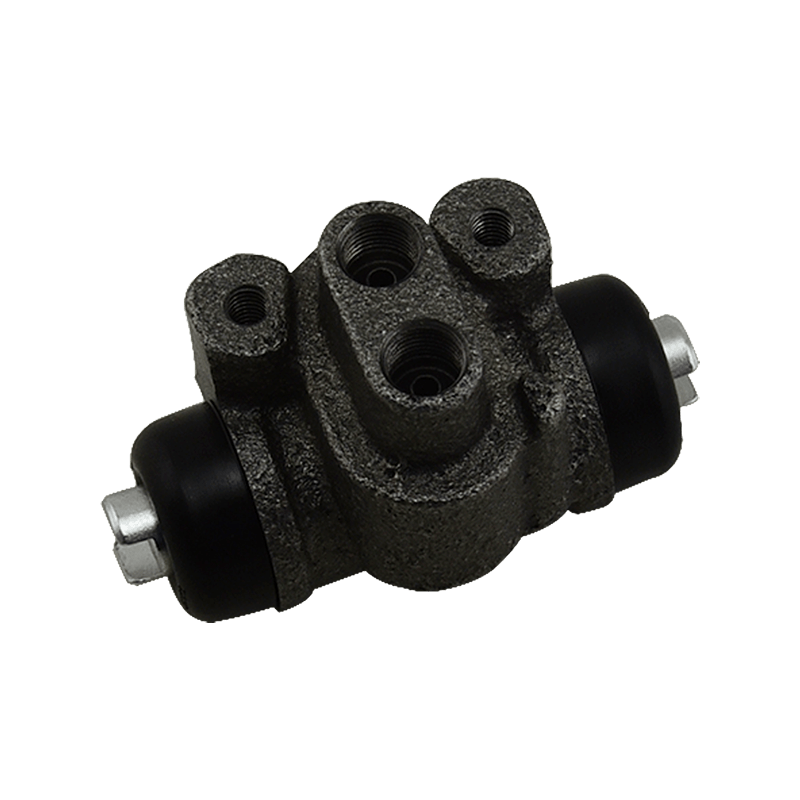
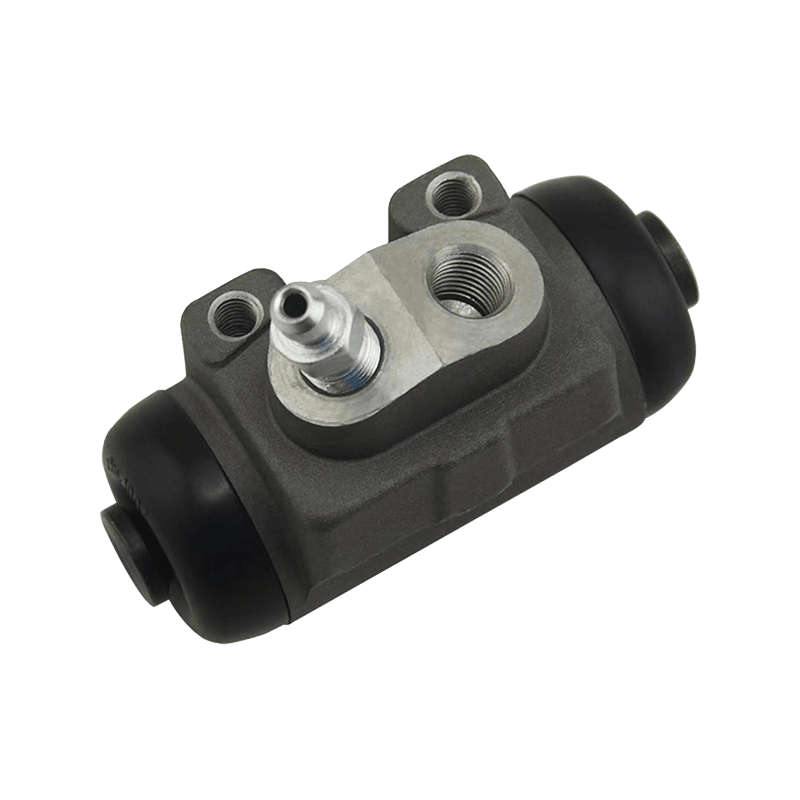
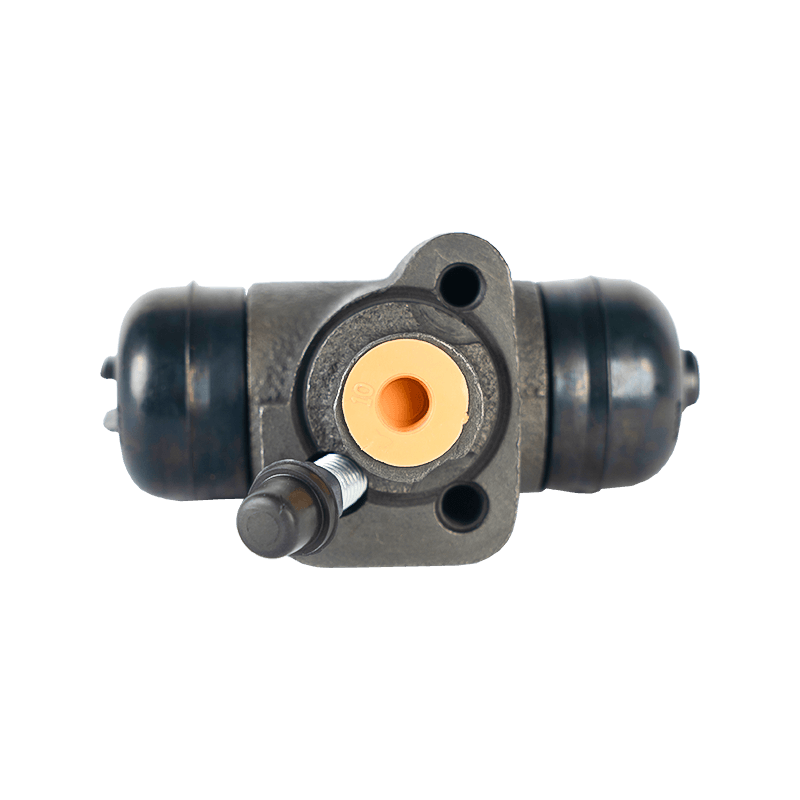
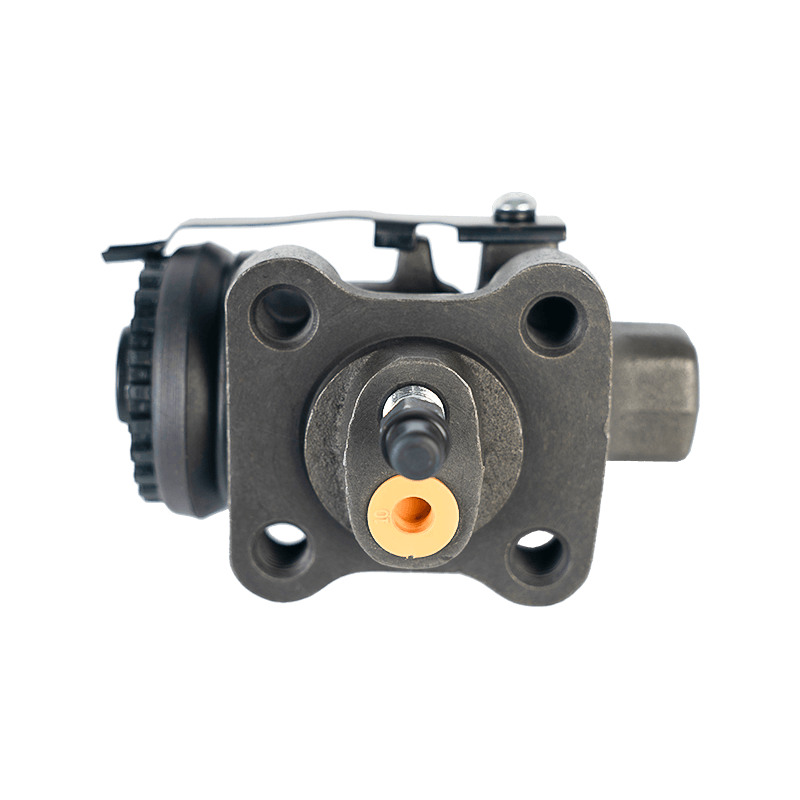
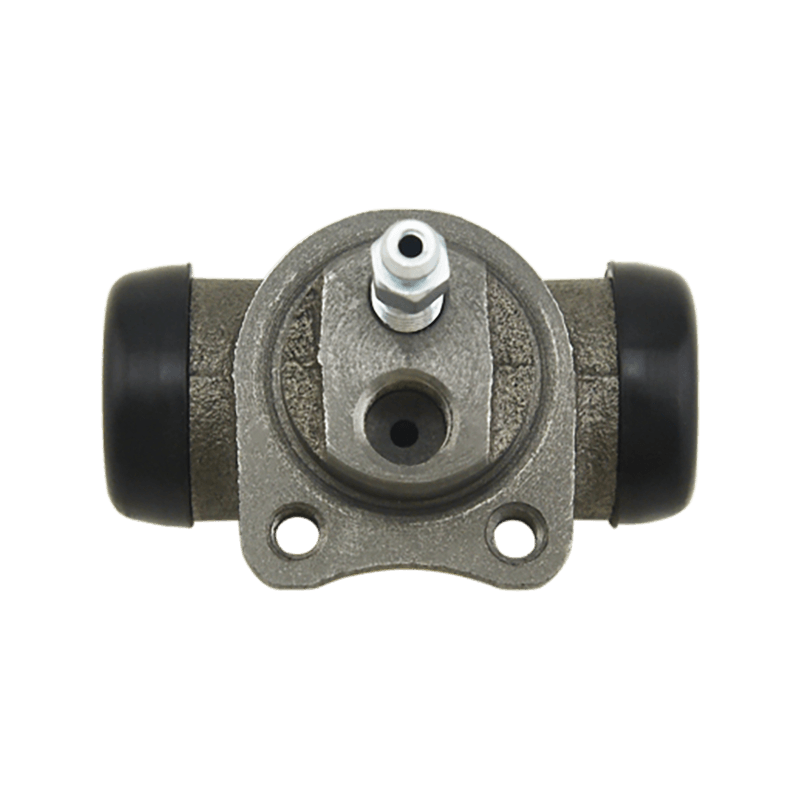
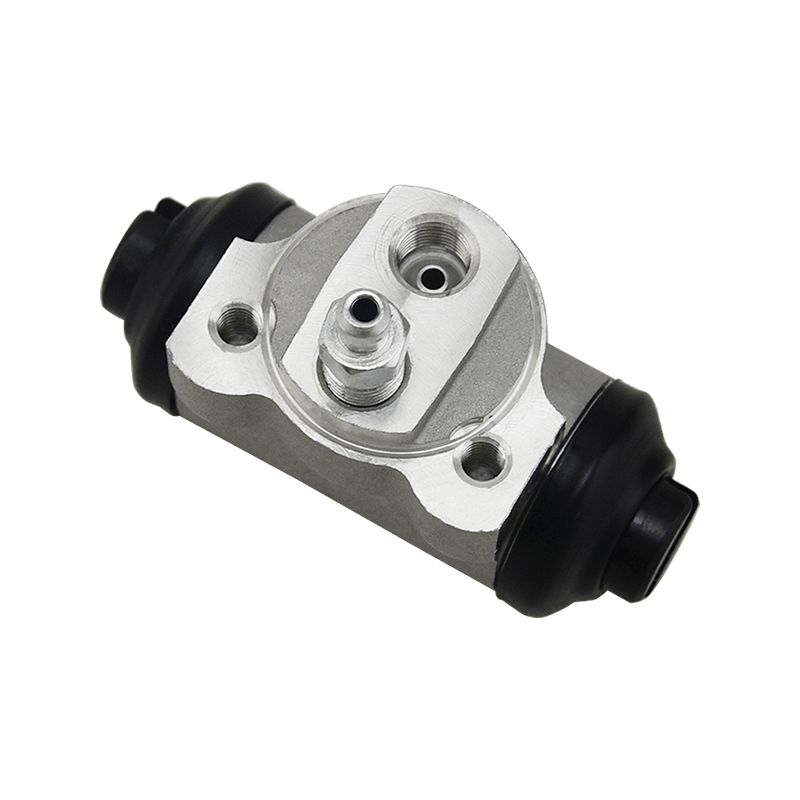
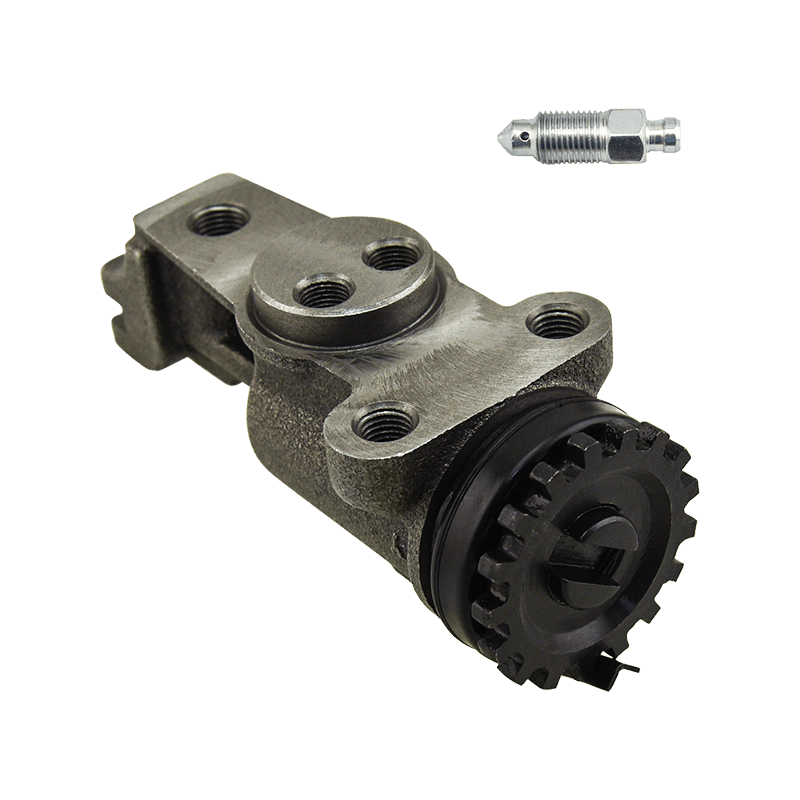
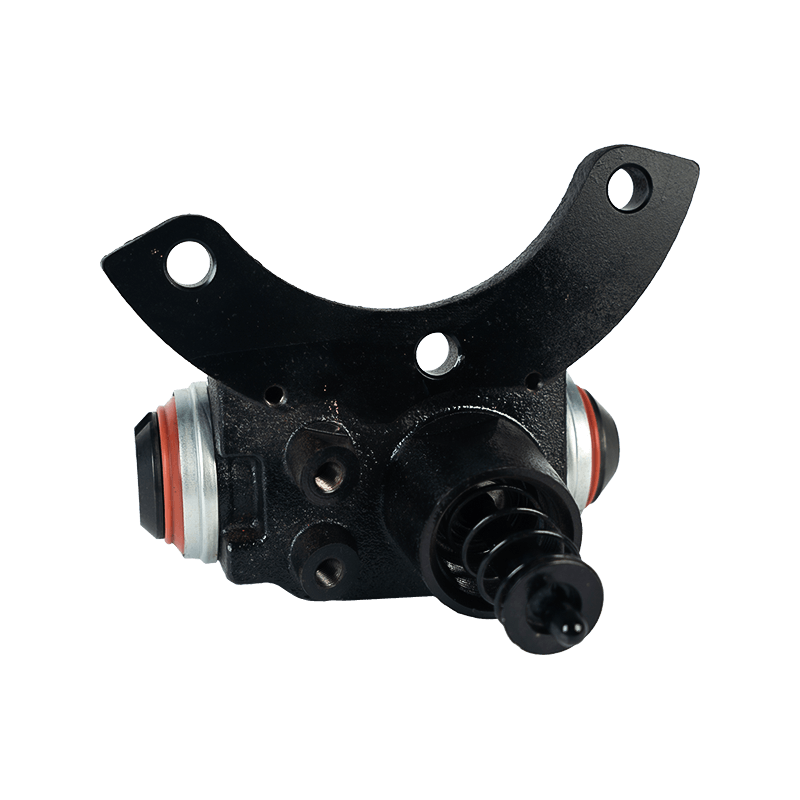
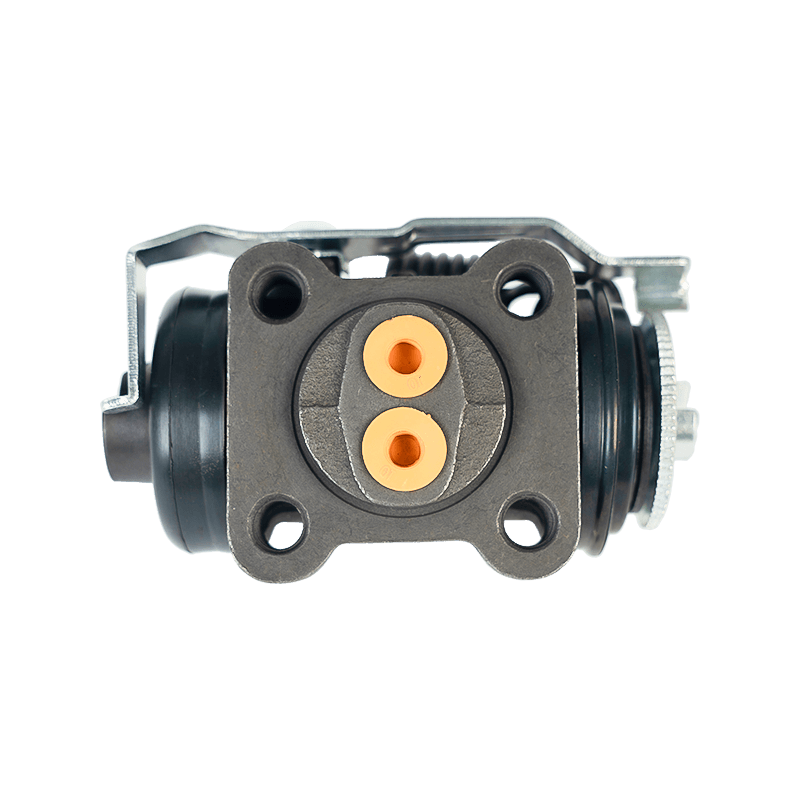
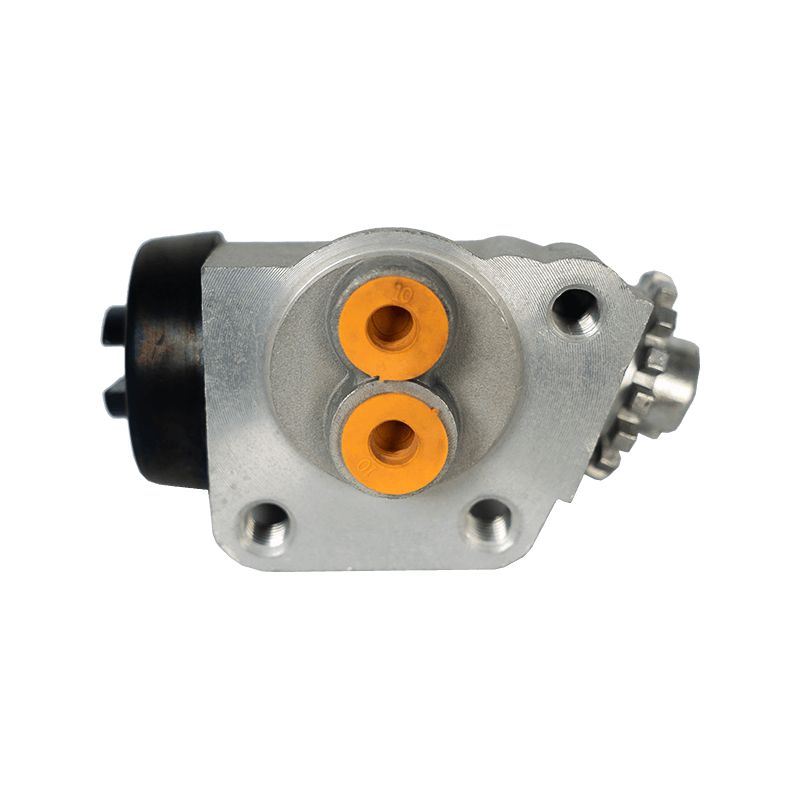
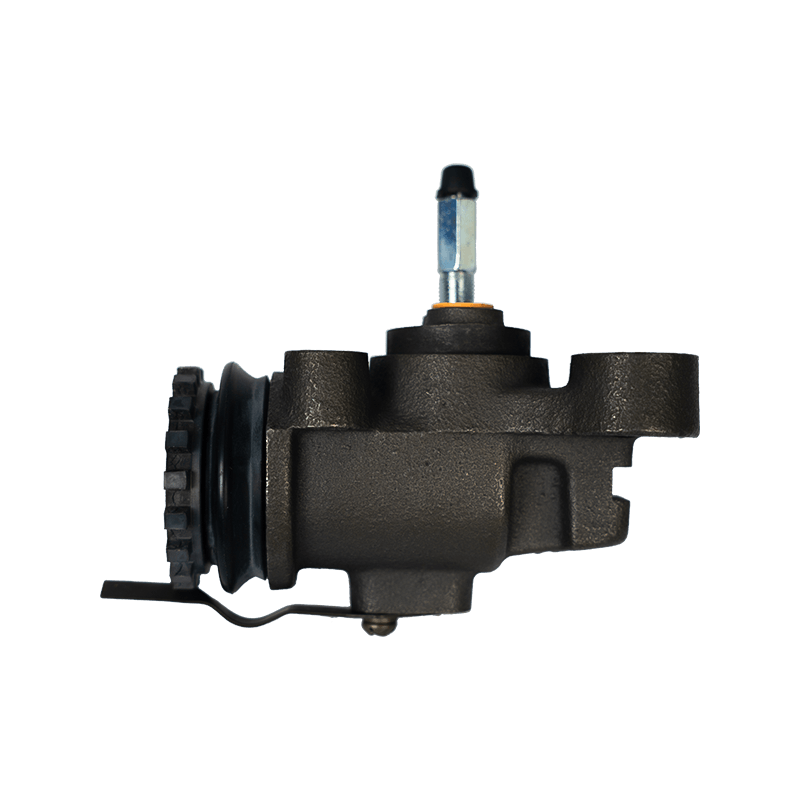
The core function of the brake wheel cylinder is to convert the hydraulic energy transmitted by the brake master cylinder into mechanical thrust, drive the brake shoe or brake pad to rub against the rotating parts (such as brake drum or brake disc), so as to achieve vehicle deceleration or parking. When the driver steps on the brake pedal, the hydraulic pressure generated by the vacuum booster and the master cylinder is pressed into the wheel cylinder cavity through the pipeline, pushing the internal piston to extend outward, forcing the brake shoe to open or the brake pad to clamp, and finally converting the vehicle's kinetic energy into heat energy dissipation through friction.
Depending on the type of brake, the brake wheel cylinder is mainly divided into two structures: single piston type and double piston type. The single piston type is mostly used for double leading shoe or double following shoe brakes, and the contact between the friction plate and the brake drum is achieved through unidirectional thrust; while the double piston type is adapted to more complex braking scenarios with a symmetrical layout, such as leading and following shoe type, two-way double leading shoe type and two-way self-enhancing brake. The internal design of the double piston wheel cylinder is precise, and the two pistons work together with the spring to ensure that the brake shoe responds quickly under the action of hydraulic pressure and the pressure is evenly distributed. When the hydraulic oil enters the oil chamber between the two pistons, the symmetrical thrust causes the brake shoes to open synchronously, which not only improves the braking efficiency, but also avoids the phenomenon of eccentric wear caused by uneven force.
In order to ensure the reliability and sensitivity of the braking system, the brake wheel cylinder is designed with a variety of design ideas. The cylinder body is usually equipped with a bleed bolt to discharge the bubbles mixed in the hydraulic pipeline to prevent the braking force from being attenuated due to air blockage. This design is particularly important in frequent braking or high temperature environments. For example, when braking continuously on a long downhill section, the bleed function can maintain the accuracy of hydraulic transmission and avoid thermal decay of braking performance. In addition, the brake wheel cylinder is mostly made of corrosion-resistant materials and high-precision sealing technology, which not only reduces weight but also extends service life, and is suitable for the diverse needs from family cars to heavy trucks.
 Search
Search
 Eng
Eng 
 English
English Español
Español Português
Português