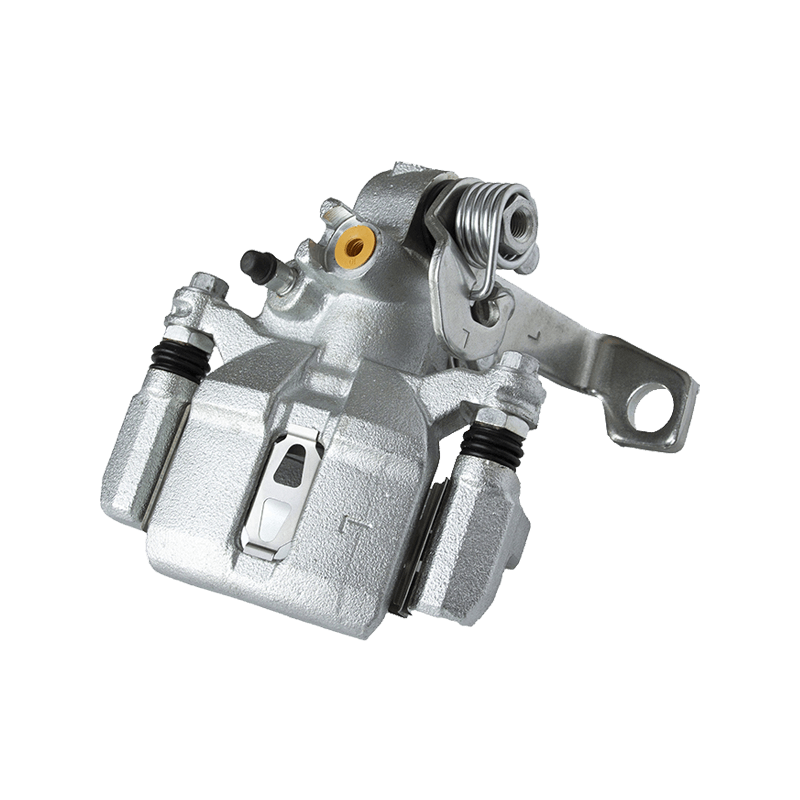
When do you need to replace your brake calipers?
 2025.09.25
2025.09.25
 Industry News
Industry News
The brake caliper is the core component of the vehicle's braking system. The condition of the brake caliper directly affects driving safety. When the following situations occur, the brake caliper must be replaced in time to avoid brake failure or causing greater faults:
1. 7 situations where the brake caliper must be replaced
(1). Brake caliper piston stuck
Symptoms: Abnormal drag on one side of the wheel during driving (wheel hub heats up, fuel consumption increases). The brake pad cannot return to its original position after releasing the brake, resulting in abnormal wear of the brake pad (inside/outside uneven wear). Detection method: Use a jack to lift the wheel and manually rotate the tire. Normally, it should be able to rotate easily (without braking). If there is obvious resistance, the piston may be stuck.
(2). Brake fluid leakage
Warning signal: There are oil stains on the surface of the brake caliper or the inside of the wheel hub (the brake fluid is light yellow and has a pungent odor). The brake pedal becomes soft, the stroke becomes longer, and it may even take the pedal to the bottom to brake.
Note: Leakage is mostly caused by aging of the piston seal or cracks in the caliper body, and must be replaced immediately (leakage will cause brake failure).
(3). Deformation or cracking of the caliper body
Cause: Severe impact (such as hitting the curb) and long-term overload braking leading to metal fatigue.
Symptom: Steering wheel shakes when braking (this needs to be distinguished from brake disc deformation). Visible cracks or obvious deformation of the caliper body (especially the guide pin of the floating caliper).
(4) Damaged piston dust boot Consequences
Dust/water enters the piston cavity, accelerating the corrosion of the seal ring, and eventually causing the piston to become stuck (common in vehicles that wade through water). Inspection: After removing the tire, observe whether the dust boot is cracked or falling off (the life of rubber parts is usually 50,000-80,000 kilometers).
(5) Guide pin stuck Symptoms
Abnormal noise during braking (metal friction sound), insufficient braking force on one side. After removing the brake caliper, the guide pin cannot be easily pulled out by hand or slides poorly. Treatment: If lubrication or replacement of the guide pin is still ineffective, the brake caliper needs to be replaced as a whole (mostly seen in vehicles that have not been maintained for a long time).
(6) Poor return of the brake caliper Symptoms
Premature wear of the brake pad (wear out after 20,000-30,000 kilometers), abnormal scratches on the brake disc. The wheel continues to heat up after braking, and even smokes. Cause: Return spring failure or hydraulic system pressure cannot be released (need to check the synchronization of the brake master cylinder).
(7). Severe rust
High-incidence environment: High humidity/salt-alkali area or long-term parking of vehicles.
Judgment standard: Caliper body rust depth > 1mm, or rust area exceeds 30%. Rust inside the piston cavity causes brake fluid contamination (liquid level sensor alarm).

2. Temporary emergency and replacement suggestions
(1). When can it be temporarily not replaced: Slight oil leakage but braking performance has not decreased (need to closely observe the fluid level). The guide pin is slightly stuck and returns to normal after cleaning and lubrication.
(2). Replacement principle: Replace in pairs. Even if only one side is damaged, it is recommended to replace both sides at the same time (to ensure balanced braking force). Original parts are preferred: Aftermarket calipers may have problems such as insufficient material strength and large piston tolerance.
3. Necessary inspections after replacement
Brake system emptying: Use special tools to completely exhaust the air (it is recommended to use a circulating machine to change the oil) to avoid air blockage. Brake Pad Break-in: New calipers require a gentle break-in period of 200-300 kilometers, avoiding sudden braking.
Torque Recheck: Mounting bolts must be tightened according to the torque specified in the service manual.
4. Preventive Maintenance Recommendations
Every 2 years or 40,000 kilometers: Check the lubrication of the brake caliper sliding parts (use a dedicated silicone-based grease).
After wading through water: Clean the brake caliper promptly to prevent sediment buildup.
When replacing brake pads: Clean the pistons and inspect the integrity of the dust boots.
Stop immediately and call for assistance if any of the following occur during braking:
The brake pedal suddenly collapses (complete hydraulic system failure).
Smoke or fire appears at the wheel (complete caliper lock). Promptly replacing a damaged brake caliper can avoid more expensive repairs (such as damage to the brake disc or bearing) and the risk of a traffic accident.
 Search
Search
 Eng
Eng 
 English
English Español
Español Português
Português