Why Choose OE Quality Brake Pads? When selecting brake pads, OE QUALITY BRAKE PADS ensure precise fit, optimal braking performance, and long-term durability. Unlike generic pads, OE pads are engineered to meet the origi...
READ MORE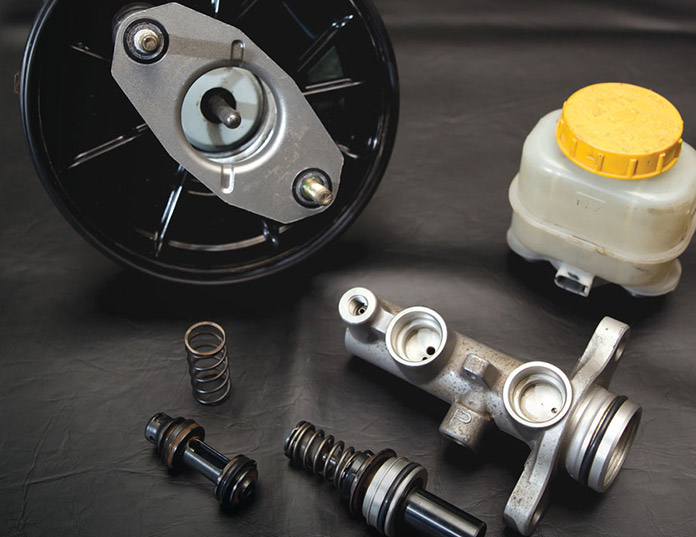
We have more than 1,000 brake shoes and brake pads for European, American, Russian, Japanese and Korean cars. The associated factories have created a highly experienced manufacturing team that exports thousands of auto part products worldwide. High quality and competitive prices are our targets. Our products have gained the certifications of ISO9001 and TS16949. We have built up a solid reputation with our customers in more than 30 countries.
We are looking forward to having a brighter and more successful business in the near future together with all of our clients all over the world.
-
-
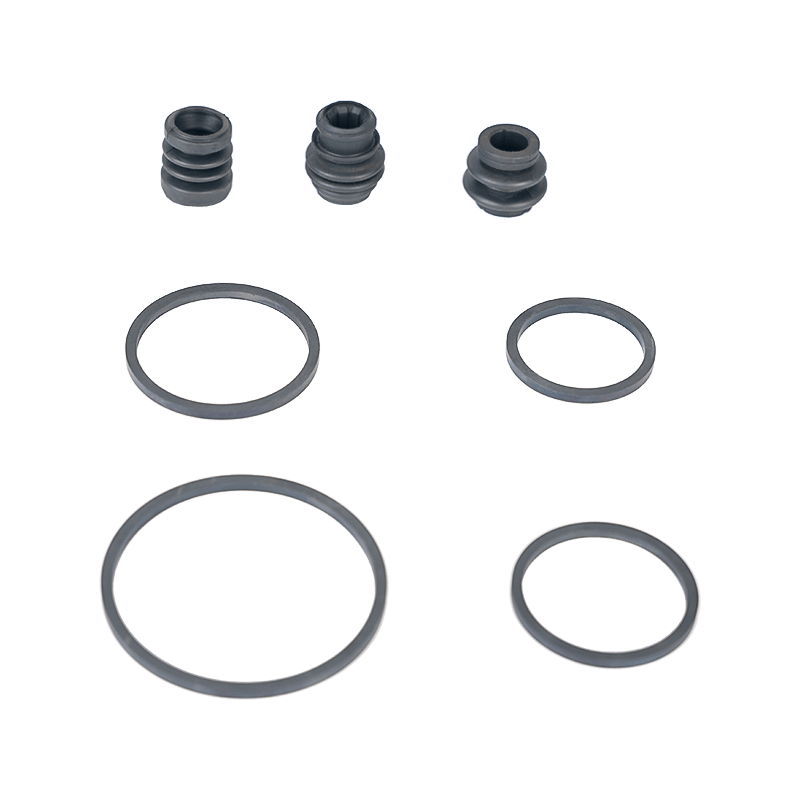
What is a Hydraulic Brake Master Cylinder? The hydraulic brake master cylinder is a critical component in a vehicle's braking system. It converts the force applied to the brake pedal into hydraulic pressure, which is th...
READ MORE -
Why OE Quality Brake Pads Are the Best Choice for Your Car OE (Original Equipment) quality brake pads are specifically designed to match the specifications and performance standards set by the vehicle manufacturer. They...
READ MORE
As the core guarantee system for vehicle safety, the function of the automotive brake system depends on the precise coordination and technological innovation of multiple automotive brake system accessories. From the basic friction pair to the cutting-edge electronic control system, the design of each accessory carries the mission of kinetic energy conversion, dynamic control and safety assurance, and together builds a safety line of defense for modern transportation.
The brake master cylinder and wheel cylinder constitute the power transmission chain of hydraulic braking. When the driver steps on the pedal, the vacuum booster amplifies the foot force, pushes the master cylinder piston to compress the brake fluid, and transmits the pressure evenly to each wheel brake through Pascal's law. As the execution terminal, the wheel cylinder pushes the friction element to contact the rotating part through the piston, converting the hydraulic energy into mechanical force. In the disc brake, the floating caliper drives the friction plate through the unilateral piston, and the reaction force drives the caliper body to slide to achieve bidirectional clamping; while the fixed multi-piston caliper optimizes the braking force distribution through symmetrical pressure.
The combination of brake disc and brake pad is the core of kinetic energy conversion. The open design of the disc brake accelerates airflow and heat dissipation through ventilation slots and perforated structures. The ceramic composite brake disc can withstand high temperatures of 1400°C, reducing weight by 50% compared to traditional cast iron discs while extending life to 300,000 kilometers, becoming a standard feature of high-performance models. Brake pad materials have evolved from asbestos and semi-metal to ceramic formulas, and the composite structure of carbon fiber and ceramic fiber achieves a balance between high-temperature stability and quietness.
 Search
Search
 Eng
Eng 
 English
English Español
Español Português
Português